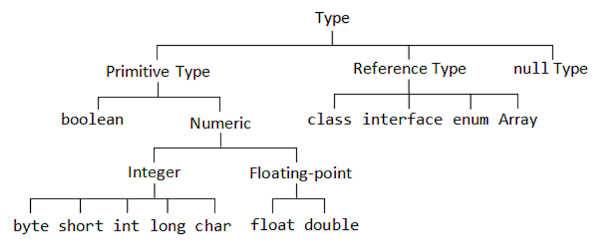
- 자바에서 제공하는 데이터 타입은 크게
primitive type과reference type, 그리고null type으로 나눌 수 있음.
- 총 8가지의
primitive type을 미리 정의하여 제공함. primitive type은 기본값을 가지고 있기 때문에 null값을 가질 수 없음.- 실제로 자바에서 값을 저장하는 공간으로 stack 메모리에 저장됨.
| Data Type | Size | Default Value | Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| boolean | 1 bit | false | true, false |
| byte | 1 byte | 0 | -128 ~ 127 |
| char | 2 byte | '\u0000' | 0 ~ 65535 |
| short | 2 byte | 0 | -32768 ~ 32767 |
| int | 4 byte | 0 | -2147483648 ~ 2147483647 |
| long | 8 byte | 0L | -9223372036854775808 ~ 9223372036854775807 |
| float | 4 byte | 0.0f | 1.4e-45 ~ 3.4028235e+38 |
| double | 8 byte | 0.0d | 4.9e-324 ~ 1.7976931348623157e+308 |
primitive type을 제외한 모든 타입은reference type으로 분류됨.- null값을 가질 수 있음.
- 주소값을 저장하는 공간으로 heap 메모리에 저장됨. heap 영역에
Object를 가리키는 reference 변수가 stack 영역에 생성됨.
| Data Type | Default Value |
|---|---|
| Enumeration | null |
| Array | null |
| Class | null |
| Interface | null |
- Wrapper Class는
primitive type을reference type처럼 사용하기 위한 클래스를 의미함. - Java의 모든
primitive type은 각각의 Wrapper Class를 가지며 값을 가지는 객체를 생성할 수 있음.
| Primitive Type | Wrapper Class |
|---|---|
| boolean | Boolean |
| byte | Byte |
| char | Character |
| short | Short |
| int | Integer |
| long | Long |
| float | Float |
| double | Double |
- 또한, wrapper class로 감싸고 있는
primitive type의 값은 외부에서 변경할 수 없음.
// wrapper class is immutable
Integer i = 10; // Integer i = new Integer(10);
i = 11; // i = new Integer(11);- 객체의 값을 변경하는 것이 아닌 새로운 객체를 가리키게 함.
- 모든 wrapper class의 부모 클래스는
Object클래스이며 숫자를 다루는 클래스들의 부모 클래스는Number클래스임.
- 가장 큰 이유는 제네릭 때문임.
primitive type은 객체가 아니며 언어 자체에 정의되어 있음. 따라서 경우에 따라 데이터 타입은 객체로 변환해야 할 필요성이 있음. 예를 들어,Collection객체에 정수형 변수를 포함시켜야 하는 경우 제네릭을 통해 타입을 지정해주어야 하는데primitive type의 변수는 객체가 아니기 때문에 포함시킬 수 없음. 이때 필요한 것이Wrapper Class임.
// List
public interface List<E> extends Collection<E>
// ArrayList<Integer>
List<int> list = new ArrayList<>(); // compile error
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); // compile success- 또 다른 이유로는
primitive type에 null값을 넣기 위해서임.primitive type은 null값을 가질 수 없기 때문에Wrapper Class를 사용함.
// primitive type
int i = null; // compile error
// wrapper class
Integer i = null; // compile success- 마지막으로 Wrapper Class를 사용하면
primitive type을 객체로 포장하여 다양한 메소드를 사용할 수 있음.
Integer i = 10;
Double d = i.doubleValue();- Wrapper Class를 사용하는 방법은 다음과 같음.
Integer i = new Integer(10);
Integer j = Integer.valueOf(10 /* or "10" */);
Integer k = Integer.parseInt("10");
// parseBoolean, parseByte, parseShort, parseLong, parseFloat, parseDouble- Wrapper Class의 생성자와 static method를 통해
primitive type을Wrapper Class로 변환할 수 있음. 이를Boxing이라고 함. Unboxing의 경우Boxing의 반대 개념으로Wrapper Class를primitive type으로 변환하는 것임.
Integer i = new Integer(10);
int j = i.intValue();
// booleanValue, byteValue, shortValue, longValue, floatValue, doubleValue- JDK1.5 부터는
Auto Boxing과Auto Unboxing이라는 기능이 추가됨. 이는boxing과unboxing을 자동으로 처리해주는 기능임.
// Auto-Boxing
Integer i = 10;
// Auto-Unboxing
int j = i + 1;
primitive type인boolean의 Wrapper Class.
public final class Boolean implements java.io.Serializable,
Comparable<Boolean>
{
public static final Boolean TRUE = new Boolean(true);
public static final Boolean FALSE = new Boolean(false);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static final Class<Boolean> TYPE = (Class<Boolean>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("boolean");
private final boolean value;
// Serializable을 상속하는 클래스이기 때문에 Class의 versioning을 위한 UID를 정의해야 함.
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3665804199014368530L;
// Auto-Boxing이 나온 뒤로 생성자를 사용한 방식이 deprecated되었음.
@Deprecated(since="9")
public Boolean(boolean value) {
this.value = value;
}
// 상동
@Deprecated(since="9")
public Boolean(String s) {
this(parseBoolean(s));
}
public static boolean parseBoolean(String s) {
return "true".equalsIgnoreCase(s);
}
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public boolean booleanValue() {
return value;
}
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public static Boolean valueOf(boolean b) {
return (b ? TRUE : FALSE);
}
public static Boolean valueOf(String s) {
return parseBoolean(s) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
public static String toString(boolean b) {
return b ? "true" : "false";
}
public String toString() {
return value ? "true" : "false";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Boolean.hashCode(value);
}
public static int hashCode(boolean value) {
return value ? 1231 : 1237;
}
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Boolean) {
return value == ((Boolean)obj).booleanValue();
}
return false;
}
public static boolean getBoolean(String name) {
boolean result = false;
try {
result = parseBoolean(System.getProperty(name));
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | NullPointerException e) {
}
return result;
}
public int compareTo(Boolean b) {
return compare(this.value, b.value);
}
public static int compare(boolean x, boolean y) {
return (x == y) ? 0 : (x ? 1 : -1);
}
public static boolean logicalAnd(boolean a, boolean b) {
return a && b;
}
public static boolean logicalOr(boolean a, boolean b) {
return a || b;
}
public static boolean logicalXor(boolean a, boolean b) {
return a ^ b;
}
}
primitive type인char의 Wrapper Class.
abstract class CharacterData {
abstract int getProperties(int ch);
abstract int getType(int ch);
abstract boolean isDigit(int ch);
abstract boolean isLowerCase(int ch);
abstract boolean isUpperCase(int ch);
abstract boolean isWhitespace(int ch);
abstract boolean isMirrored(int ch);
abstract boolean isJavaIdentifierStart(int ch);
abstract boolean isJavaIdentifierPart(int ch);
abstract boolean isUnicodeIdentifierStart(int ch);
abstract boolean isUnicodeIdentifierPart(int ch);
abstract boolean isIdentifierIgnorable(int ch);
abstract int toLowerCase(int ch);
abstract int toUpperCase(int ch);
abstract int toTitleCase(int ch);
abstract int digit(int ch, int radix);
abstract int getNumericValue(int ch);
abstract byte getDirectionality(int ch);
//need to implement for JSR204
int toUpperCaseEx(int ch) {
return toUpperCase(ch);
}
char[] toUpperCaseCharArray(int ch) {
return null;
}
boolean isOtherLowercase(int ch) {
return false;
}
boolean isOtherUppercase(int ch) {
return false;
}
boolean isOtherAlphabetic(int ch) {
return false;
}
boolean isIdeographic(int ch) {
return false;
}
// Character <= 0xff (basic latin) is handled by internal fast-path
// to avoid initializing large tables.
// Note: performance of this "fast-path" code may be sub-optimal
// in negative cases for some accessors due to complicated ranges.
// Should revisit after optimization of table initialization.
static final CharacterData of(int ch) {
if (ch >>> 8 == 0) { // fast-path
return CharacterDataLatin1.instance;
} else {
switch(ch >>> 16) { //plane 00-16
case(0):
return CharacterData00.instance;
case(1):
return CharacterData01.instance;
case(2):
return CharacterData02.instance;
case(14):
return CharacterData0E.instance;
case(15): // Private Use
case(16): // Private Use
return CharacterDataPrivateUse.instance;
default:
return CharacterDataUndefined.instance;
}
}
}
}- 숫자를 다루는 Wrapper Class들의 부모 클래스.
- 추상 클래스로, 추상 메소드들을 가지고 있으며, 이를 상속받아 구현하는 클래스들이 존재한다.
public abstract class Number implements java.io.Serializable {
public abstract int intValue();
public abstract long longValue();
public abstract float floatValue();
public abstract double doubleValue();
public byte byteValue() {
return (byte)intValue();
}
public short shortValue() {
return (short)intValue();
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = -8742448824652078965L;
}primitive type인int의 Wrapper Class.
public final class Integer extends Number implements Comparable<Integer> {
@Native public static final int MIN_VALUE = 0x80000000;
@Native public static final int MAX_VALUE = 0x7fffffff;
public static final Class<Integer> TYPE = (Class<Integer>) Class.getPrimitiveClass("int");
static final char[] digits = {
'0' , '1' , '2' , '3' , '4' , '5' ,
'6' , '7' , '8' , '9' , 'a' , 'b' ,
'c' , 'd' , 'e' , 'f' , 'g' , 'h' ,
'i' , 'j' , 'k' , 'l' , 'm' , 'n' ,
'o' , 'p' , 'q' , 'r' , 's' , 't' ,
'u' , 'v' , 'w' , 'x' , 'y' , 'z'
};
public static String toString(int i, int radix) {
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX || radix > Character.MAX_RADIX)
radix = 10;
/* Use the faster version */
if (radix == 10) {
return toString(i);
}
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] buf = new byte[33];
boolean negative = (i < 0);
int charPos = 32;
if (!negative) {
i = -i;
}
while (i <= -radix) {
buf[charPos--] = (byte)digits[-(i % radix)];
i = i / radix;
}
buf[charPos] = (byte)digits[-i];
if (negative) {
buf[--charPos] = '-';
}
return StringLatin1.newString(buf, charPos, (33 - charPos));
}
return toStringUTF16(i, radix);
}
static final byte[] DigitTens = {
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1', '1',
'2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2', '2',
'3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3', '3',
'4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4', '4',
'5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5', '5',
'6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6', '6',
'7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7', '7',
'8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8', '8',
'9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9', '9',
} ;
static final byte[] DigitOnes = {
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
'0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9',
} ;
@HotSpotIntrinsicCandidate
public static String toString(int i) {
int size = stringSize(i);
if (COMPACT_STRINGS) {
byte[] buf = new byte[size];
getChars(i, size, buf);
return new String(buf, LATIN1);
} else {
byte[] buf = new byte[size * 2];
StringUTF16.getChars(i, size, buf);
return new String(buf, UTF16);
}
}
static int getChars(int i, int index, byte[] buf) {
int q, r;
int charPos = index;
boolean negative = i < 0;
if (!negative) {
i = -i;
}
// Generate two digits per iteration
while (i <= -100) {
q = i / 100;
r = (q * 100) - i;
i = q;
buf[--charPos] = DigitOnes[r];
buf[--charPos] = DigitTens[r];
}
// We know there are at most two digits left at this point.
q = i / 10;
r = (q * 10) - i;
buf[--charPos] = (byte)('0' + r);
// Whatever left is the remaining digit.
if (q < 0) {
buf[--charPos] = (byte)('0' - q);
}
if (negative) {
buf[--charPos] = (byte)'-';
}
return charPos;
}
/* ... */
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
if (s == null) {
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
boolean negative = false;
int i = 0, len = s.length();
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (len > 0) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(0);
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+') {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
if (len == 1) { // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
i++;
}
int multmin = limit / radix;
int result = 0;
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
int digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++), radix);
if (digit < 0 || result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
result -= digit;
}
return negative ? result : -result;
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s);
}
}
public static int parseInt(CharSequence s, int beginIndex, int endIndex, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException {
s = Objects.requireNonNull(s);
if (beginIndex < 0 || beginIndex > endIndex || endIndex > s.length()) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) {
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
boolean negative = false;
int i = beginIndex;
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (i < endIndex) {
char firstChar = s.charAt(i);
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+') {
throw NumberFormatException.forCharSequence(s, beginIndex,
endIndex, i);
}
i++;
if (i == endIndex) { // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forCharSequence(s, beginIndex,
endIndex, i);
}
}
int multmin = limit / radix;
int result = 0;
while (i < endIndex) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
int digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i), radix);
if (digit < 0 || result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forCharSequence(s, beginIndex,
endIndex, i);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forCharSequence(s, beginIndex,
endIndex, i);
}
i++;
result -= digit;
}
return negative ? result : -result;
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString("");
}
}
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseInt(s,10);
}
/* ... */
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}
/* ... */
}Wrapper Class가 JVM위에서 어떻게 관리되는지 알아보려면 아래 글을 참고하면 좋을 것 같습니다.