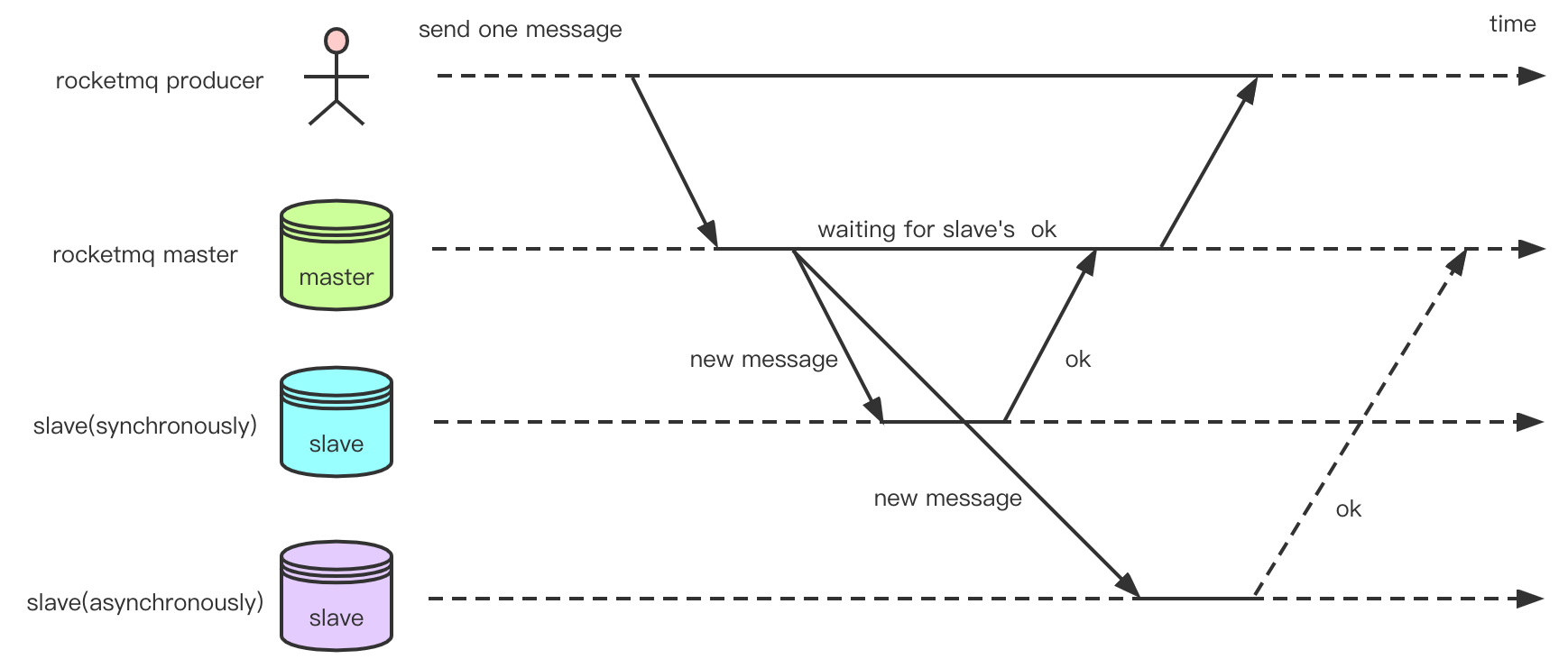
In RocketMQ, there are two main replication modes between primary and secondary servers: synchronous replication and asynchronous replication. As shown in the above figure, the replication of Slave1 is synchronous, and the Master needs to wait for Slave1 to successfully replicate the message and confirm before reporting success to the Producer. The replication of Slave2 is asynchronous, and the Master does not need to wait for the response from Slave2. In RocketMQ, if everything goes well when sending a message, the Producer client will eventually receive a PUT_OK status. If the Slave synchronization times out, it will return a FLUSH_SLAVE_TIMEOUT status. If the Slave is unavailable or the difference between the CommitLog of the Slave and Master exceeds a certain value (default is 256MB), it will return a SLAVE_NOT_AVAILABLE status. The latter two states will not cause system exceptions and prevent the next message from being written.
Synchronous replication ensures that the data can still be found in the Slave after the Master fails, which is suitable for scenarios with high reliability requirements. Although asynchronous replication may result in message loss, it is more efficient than synchronous replication because it does not need to wait for the Slave's confirmation, and is suitable for scenarios with certain efficiency requirements. However, only two modes are not flexible enough. For example, in scenarios with three or even five copies and high reliability requirements, asynchronous replication cannot meet the requirements, but synchronous replication needs to wait for each copy to confirm before returning, which seriously affects efficiency in the case of many copies. On the other hand, in the synchronous replication mode, if one of the Slaves in the copy group becomes inactive, the entire send will fail until manual processing is performed.
Therefore, RocketMQ 5 introduces quorum write for copy groups. In the synchronous replication mode, the user can specify on the broker side how many copies need to be written before returning after sending, and provides an adaptive downgrade method that can automatically downgrade based on the number of surviving copies and the CommitLog gap.
quorum write is supported by adding two parameters:
- totalReplicas:Total number of brokers in the copy replica. default is 1.
- inSyncReplicas:The number of replica groups that should normally be kept in synchronization. default is 1.
With these two parameters, you can flexibly specify the number of copies that need ACK in the synchronous replication mode.
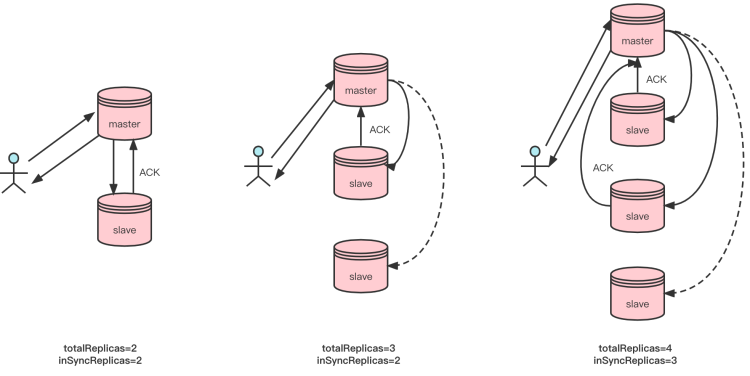
As shown in the above figure, in the case of two copies, if inSyncReplicas is 2, the message needs to be copied in both the Master and the Slave before it is returned to the client; in the case of three copies, if inSyncReplicas is 2, the message needs to be copied in the Master and any slave before it is returned to the client. In the case of four copies, if inSyncReplicas is 3, the message needs to be copied in the Master and any two slaves before it is returned to the client. By flexibly setting totalReplicas and inSyncReplicas, users can meet the needs of various scenarios.
The standards for automatic downgrade are:
- The number of surviving replicas in the current replica group
- The height difference between the Master Commitlog and the Slave CommitLog
NOTE: Automatic downgrade is only effective after the slaveActingMaster mode is enabled
The current survival information of the copy group can be obtained through the reverse notification of the Nameserver and the GetBrokerMemberGroup request, and the height difference between the Master and the Slave Commitlog can also be calculated through the position record in the HA service. The following parameters will be added to complete the automatic downgrade:
- minInSyncReplicas:The minimum number of copies in the group that must be kept in sync, only effective when enableAutoInSyncReplicas is true, default is 1
- enableAutoInSyncReplicas:The switch for automatic synchronization downgrade, when turned on, if the number of brokers in the current copy group in the synchronization state (including the master itself) does not meet the number specified by inSyncReplicas, it will be synchronized according to minInSyncReplicas. The synchronization state judgment condition is that the slave commitLog lags behind the master length by no more than haSlaveFallBehindMax. The default is false.
- haMaxGapNotInSync:The value for determining whether the slave is in sync with the master. If the slave commitLog lags behind the master length by more than this value, the slave is considered to be out of sync. When enableAutoInSyncReplicas is turned on, the smaller the value, the easier it is to trigger automatic downgrade of the master. When enableAutoInSyncReplicas is turned off and
totalReplicas == inSyncReplicas, the smaller the value, the more likely it is to cause requests to fail during high traffic. Therefore, in this case, it is appropriate to increase haMaxGapNotInSync. The default is 256K.
Note: In RocketMQ 4.x, there is a haSlaveFallbehindMax parameter, with a default value of 256MB, indicating the CommitLog height difference at which the Slave is considered unavailable. This parameter was cancelled in RIP-34.
//calculate needAckNums
int inSyncReplicas = Math.min(this.defaultMessageStore.getAliveReplicaNumInGroup(),
this.defaultMessageStore.getHaService().inSyncSlaveNums(currOffset) + 1);
needAckNums = calcNeedAckNums(inSyncReplicas);
if (needAckNums > inSyncReplicas) {
// Tell the producer, don't have enough slaves to handle the send request
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.IN_SYNC_REPLICAS_NOT_ENOUGH, null));
}
private int calcNeedAckNums(int inSyncReplicas) {
int needAckNums = this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getInSyncReplicas();
if (this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().isEnableAutoInSyncReplicas()) {
needAckNums = Math.min(needAckNums, inSyncReplicas);
needAckNums = Math.max(needAckNums, this.defaultMessageStore.getMessageStoreConfig().getMinInSyncReplicas());
}
return needAckNums;
}When enableAutoInSyncReplicas=true, the adaptive downgrade mode is enabled. When the number of surviving replicas in the replica group decreases or the height difference between the Master and the Slave Commitlog is too large, automatic downgrade will be performed, with a minimum of minInSyncReplicas replicas. For example, in two replicas, if totalReplicas=2, InSyncReplicas=2, minInSyncReplicas=1, and enableAutoInSyncReplicas=true are set, under normal circumstances, the two replicas will be in synchronous replication. When the Slave goes offline or hangs, adaptive downgrade will be performed, and the producer only needs to send to the master to succeed.
To ensure backward compatibility, users need to set the correct parameters. For example, if the user's original cluster is a two-replica synchronous replication and no parameters are modified, when upgrading to the RocketMQ 5 version, due to the default totalReplicas and inSyncReplicas both being 1, it will downgrade to asynchronous replication. If you want to maintain the same behavior as before, you need to set both totalReplicas and inSyncReplicas to 2.
references: