English | 简体中文
感觉还不错?请投出您的 Star 吧 🥰 !
来看看 FBroadcast 为开发者提供了那些不可思议的能力支持:
-
支持发送和接收指定类型的消息
-
消息支持携带任意类型数据包
-
提供环境注册,一行代码即可移除环境内所有接收者
-
不可思议的粘性广播
-
双向通信支持
-
易于构建简单明确的局部和全局状态管理
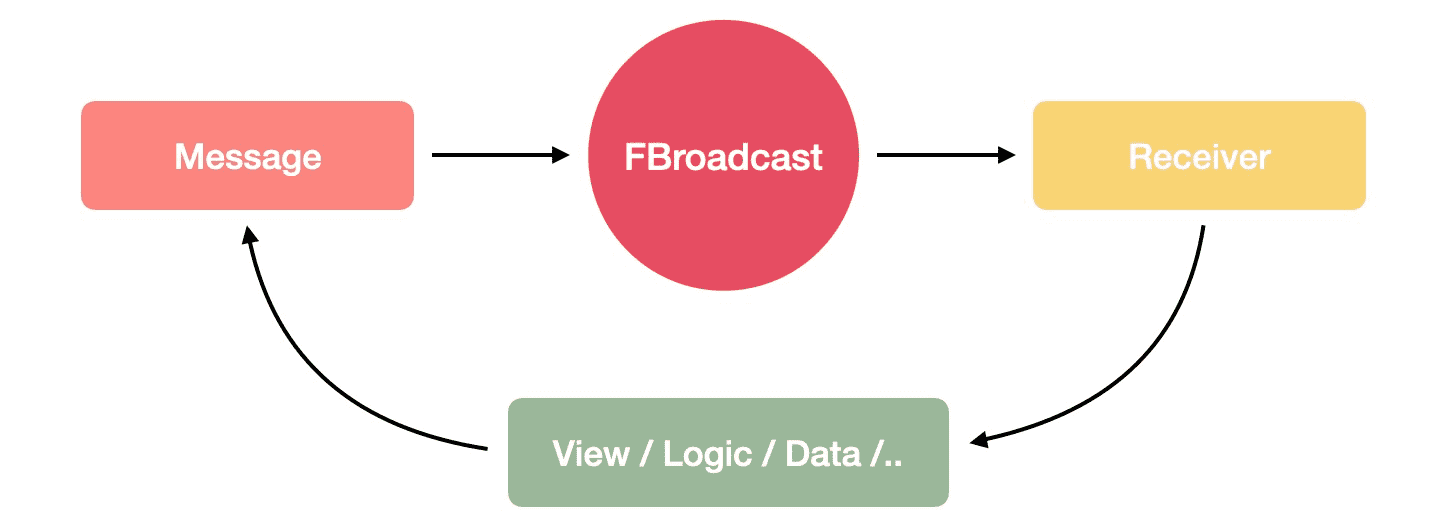
FBroadcast 是一套高效灵活的广播系统,可以帮助开发者轻松、有序的构建具有极具复杂性的关联交互和状态变化的精美应用。
FBroadcast 将为构建复杂的精美应用带来那些显而易见的改变呢?
-
Widget/模块间的完全解耦
通过 FBroadcast 高效的广播系统,开发者可以轻易的完成Widget/模块的解耦。在应用构建的时候,经常需要 Widget/模块A、B、C、.. 之间根据交互操作互相变更状态或数据,开发者们不得不为此让各个Widget/模块互相依赖或者为它们建立统一的状态管理,这能解决问题,但这让构建变得麻烦,也让变更变得难以进行。
FBroadcast 通过建立起简单、有效、明确广播系统,使得在任意Widget/模块中任意时刻/位置的改变能够主动发出广播,而需要根据这些变更作出响应或更新视图的Widget/模块只需要注册相应的信息接收器,就可以在变更发生时,接收到消息,作出响应。这使得关联模块间不再需要互相依赖,或是为它们设计建立统一的状态管理器。
十分简单,轻量,和易于变更。当一个Widget/模块不在需要根据另一个Widget/模块的变更而更新时,只需移除其中的接收器即可,而不用为此而大改依赖关系或是状态管理器。
-
简单、灵活、明确、易管理
FBroadcast 为开发者提供了可以在任意时刻发送广播,和注册/移除接收器的能力,毫无约束和灵活。
广播和接收器之间通过明确的类型(字符串)来互相确认身份,指定类型的广播,只能被指定类型的接收器接收。
FBroadcast 提供了环境注册支持,开发者可以在环境解构时,通过 [unregister()] 函数一次性移除环境中的所有类型接收器,而无需记忆和关心究竟需要移除那些接收器。例如,开发者可以在 Widget 的
dispose()中,将注册在该 Widget 中的所有接收器一次性全部移除。借助现代IDEA的能力,开发者可以为广播系统建立一张(或多张)统一的广播类型索引表,通过IDEA的引用索引,开发者可以轻松的、一目了然的看到该类型的广播在那些地方被发送过,在那些地方注册了接收器,十分易于管理和维护。而使用字符串来作为类型标识,使得开发者可以将不同类型的广播含义描述的足够清晰明白。
-
粘性广播支持
FBroadcast 提供了发送粘性广播的支持。在还没有注册任何接收器的情况下,开发者可以在事件发生时,预先发送一条粘性广播。粘性广播会被暂时滞留在广播系统中,当有接收器被注册时,即会立即广播。这有助于帮助开发者在做逻辑设计时采取更清晰有效的思路。
例如,当一个控制模块中的开关按钮被打开,而此时开关所控制的模块还没有被构建,就可以先发送一条粘性广播,在模块被构建完成注册了接收器后,就会立即接收到粘性广播而进入开启状态(这与互相依赖、定义统一状态管理或是参数传递,然后检查开关状态的思路有本质区别)。
通过 FBroadcast 来注册,发送广播非常简便。
/// 注册接收器
///
/// register
FBroadcast.instance().register(Key_Message, (value, callback) {
/// do something
});
/// 发送消息
///
/// send message
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Message);FBroadcast 允许开发者在发送消息的时候,带有数据。
/// 注册接收器
///
/// register
FBroadcast.instance().register(Key_Message, (value, callback) {
/// 获取数据
///
/// get data
var data = value;
});
/// 发送消息和数据
///
/// send message and data
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(
/// 消息类型
///
/// message type
Key_Message,
/// 数据
///
/// data
value: data,
);开发者可以选择将特定类型的消息进行持久化,这样就能轻易实现广播式的全局状态管理。
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(
/// 消息类型
///
/// message type
Key_Message,
/// 数据
///
/// data
value: data,
/// 将消息类型持久化
///
/// Persist the message types
persistence: true,
);当开发者将一个消息类型持久化后,就可以在任意位置,通过 FBroadcast.value(String key) 来获取广播系统中该类型消息的最新的数据。而更新广播系统中的数据只需要通过 broadcast() 即可完成。
⚠️ 注意,一个消息类型一旦持久化就只能通过FBroadcast.instance().clear(String key)来从广播系统中移除该类型的消息。
FBroadcast 支持开发者发送粘性广播。
FBroadcast.instance().stickyBroadcast(
/// 消息类型
///
/// message type
Key_Message,
/// 数据
///
/// data
value: data,
);当广播系统中没有对应类型的接收器时,粘性广播 将会暂时滞留在系统中,直到有该类型的接收器被注册,则会立即发出广播(当广播系统中有对应类型的接收器时,就和普通广播具有相同的表现)。
FBroadcast 支持在广播发送点接收接收器返回的消息。
/// 发送消息
///
/// send message
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(
/// 消息类型
///
/// message type
Key_Message,
/// 数据
///
/// data
value: data,
/// 接收器返回的消息
///
/// The message returned by the receiver
callback: (value){
// do something
}
);
/// 注册接收器
///
/// register
FBroadcast.instance().register(Key_Message, (value, callback) {
/// 获取数据
///
/// get data
var data = value;
/// do something
var result = logic();
/// 返回消息
///
/// return message
callback(result);
});通过 FBroadcast 能够十分轻松的实现双向通信。
FBroadcast 支持在注册接收器时传入一个环境对象(可以是任意类型),这会将接收器注册到环境中,当环境解构时,开发者可以方便的一次性移除所有在该环境中注册的接收器。
/// 注册接收器
///
/// register
FBroadcast.instance().register(
/// 消息类型
///
/// Message type
Key_Message1,
/// Receiver
///
/// Receiver
(value, callback) {
/// do something
},
/// 更多接收器
///
/// more receiver
more: {
/// 消息类型: 接收器
///
/// Message type: Receiver
Key_Message2: (value, callback) {
/// do something
},
Key_Message3: (value, callback) {
/// do something
},
Key_Message4: (value, callback) {
/// do something
},
},
/// 环境对象
///
/// context
context: this,
);
/// 移除环境中的所有接收器
///
/// Remove all receivers from the environment
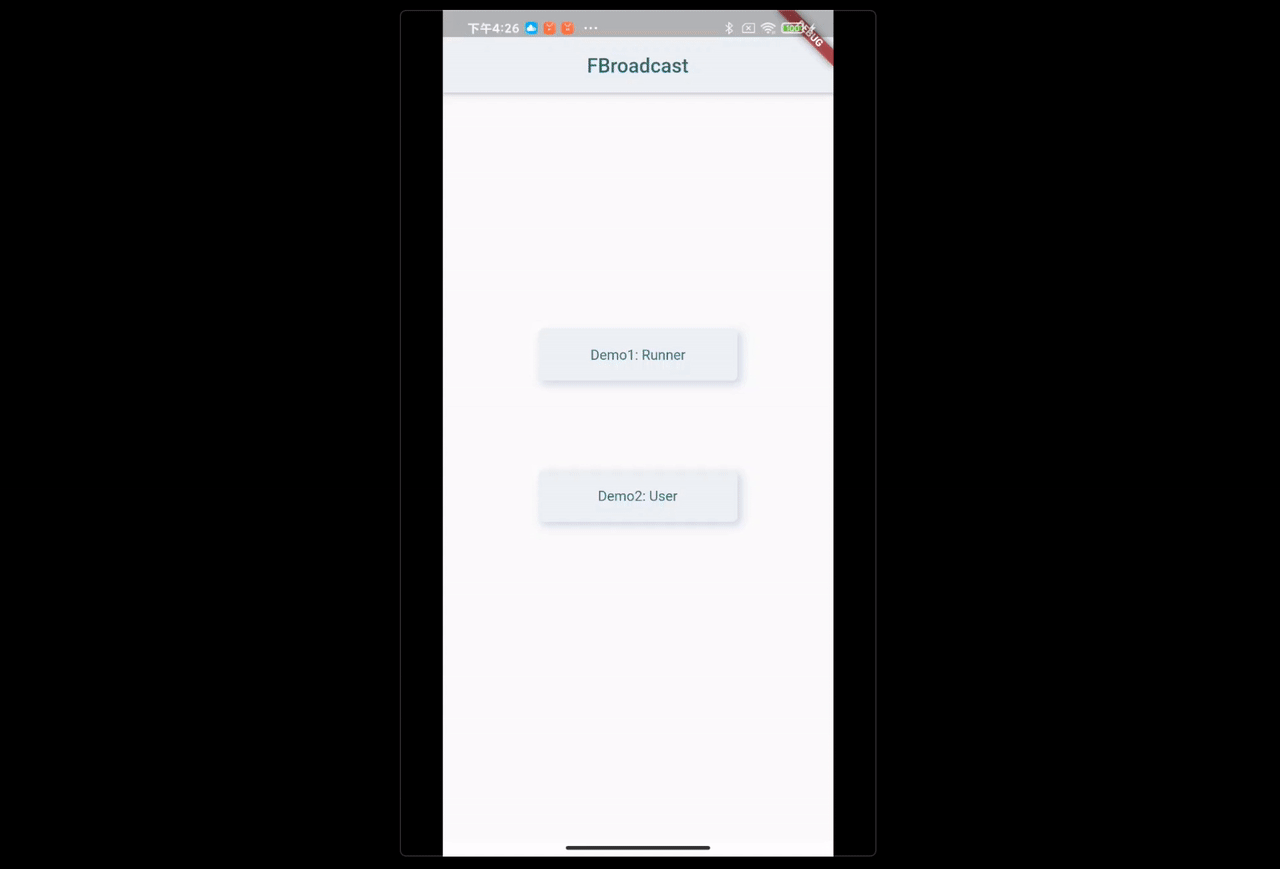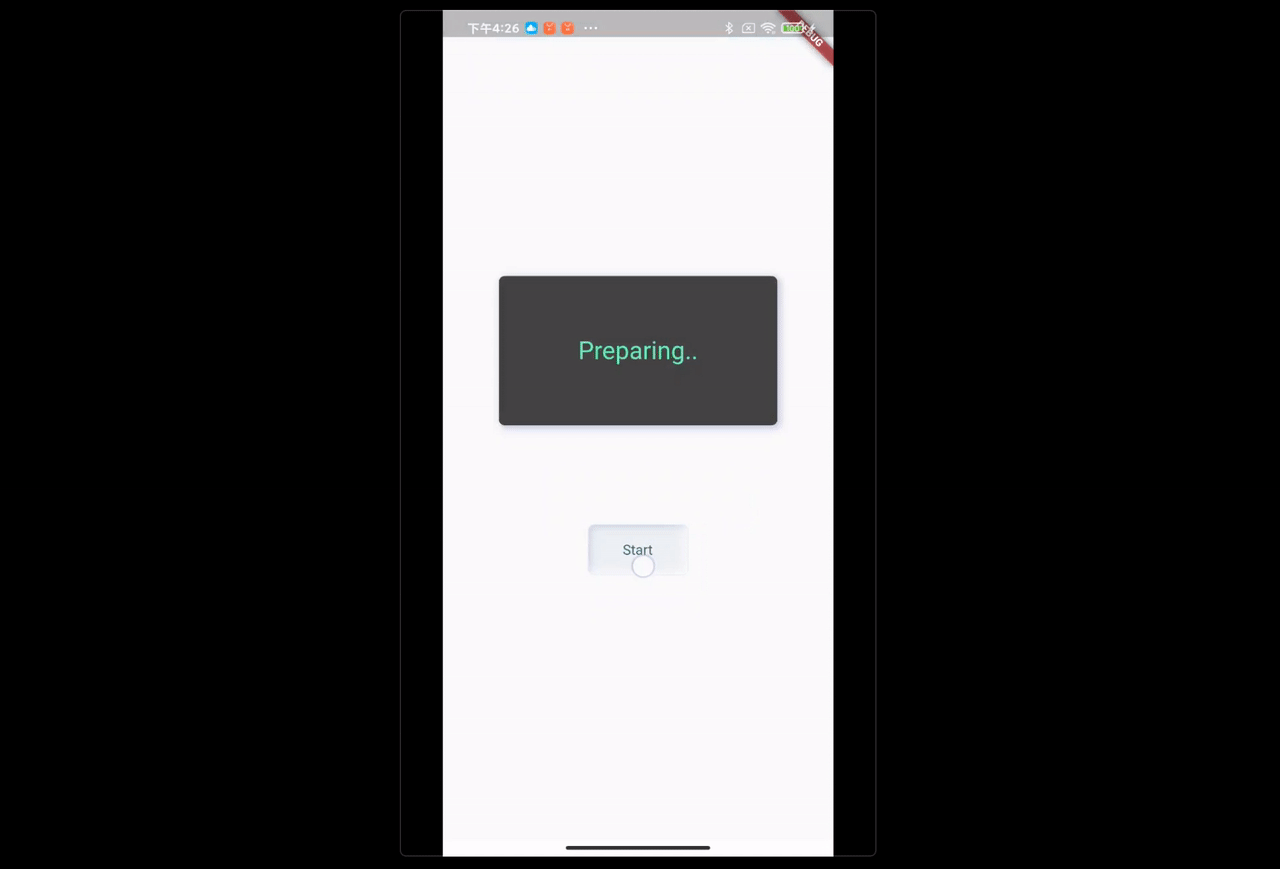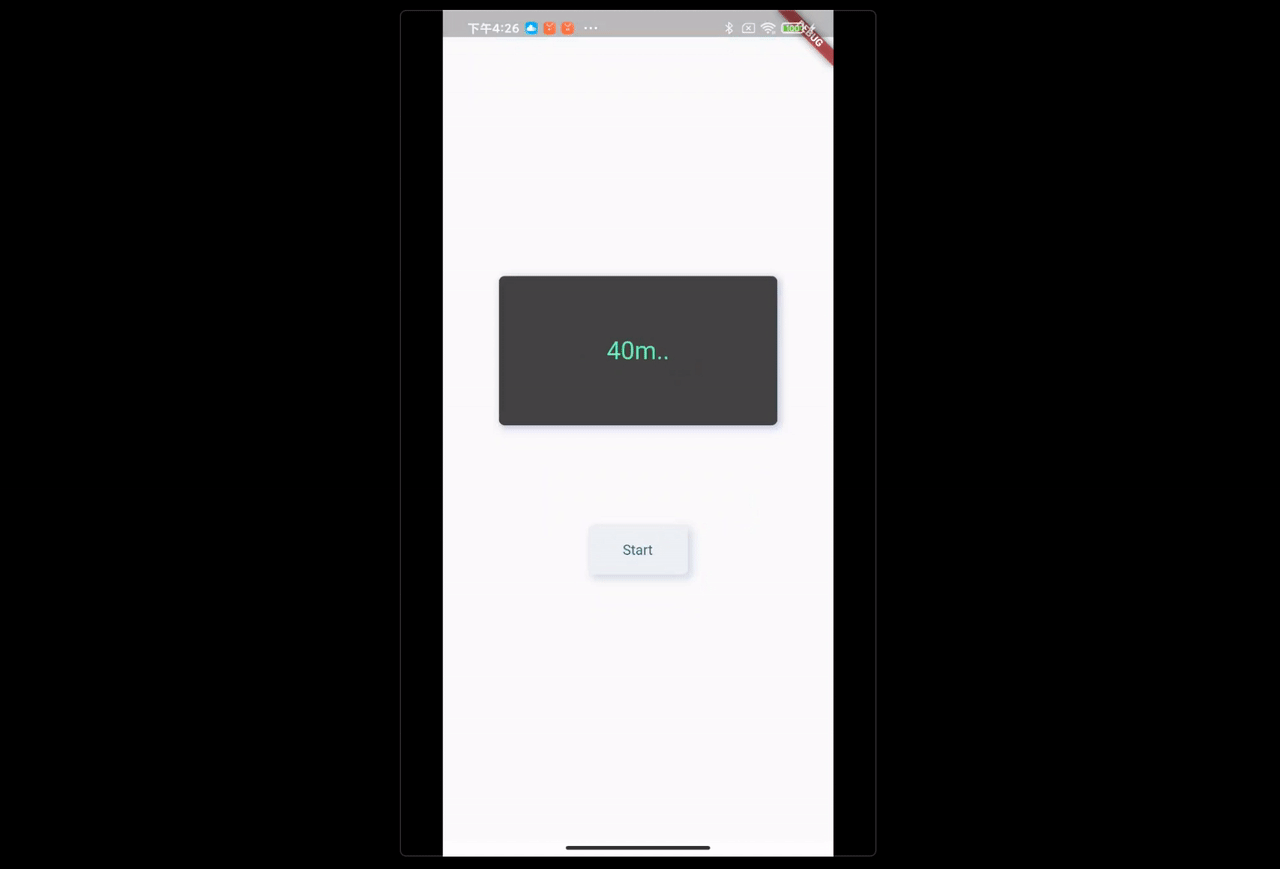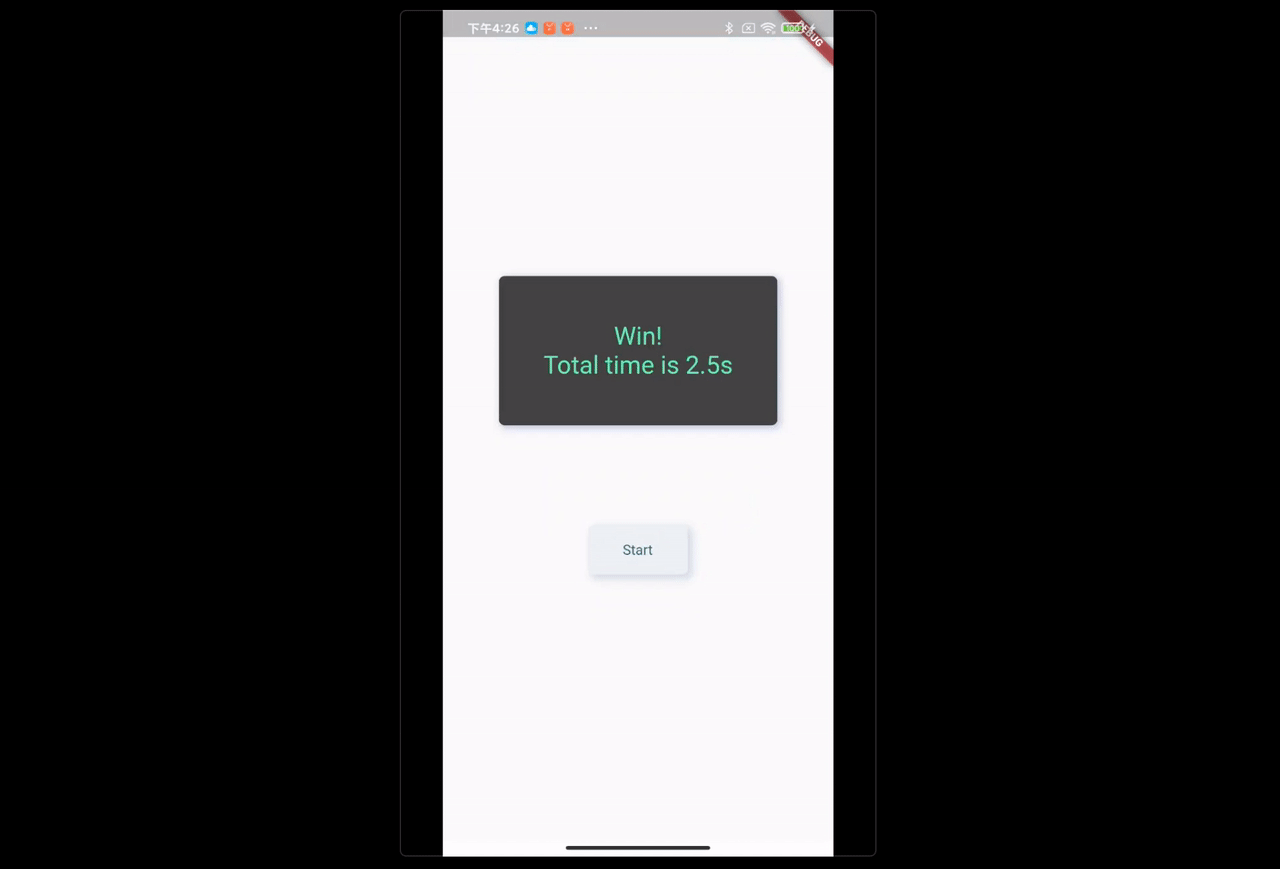
FBroadcast.instance().unregister(this);场景:点击 Start,Runner 开始 Run,显示屏需要实时更新运动员的状态。
/// Runner
class Runner {
Runner() {
/// register
FBroadcast.instance().register(Key_RunnerState, (value, callback) {
if (value is String && value.contains("Run")) {
/// receive start run message
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_RunnerState, value: "0m..");
run(20);
}
});
}
run(double distance) {
/// send running message
Timer(Duration(milliseconds: 500), () {
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_RunnerState, value: "${distance.toInt()}m..");
var newDistance = distance + 20;
if (newDistance > 100) {
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_RunnerState, value: "Win!\nTotal time is 2.5s");
} else {
run(newDistance);
}
});
}
}Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
Stateful(
/// init
initState: (setState, data) {
FBroadcast.instance().register(
Key_RunnerState,
(value, callback) {
/// refresh ui
setState(() {});
},
/// bind context
context: data,
);
},
builder: (context, setState, data) {
return FSuper(
...
/// get running message
text: FBroadcast.value(Key_RunnerState) ?? "Preparing..",
);
},
),
const SizedBox(height: 100),
FButton(
text: "Start"
...
onPressed: () {
/// send start run message
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_RunnerState, value: "Running...");
},
),
],
)在上面的示例中,通过 FBroadcast 简单清晰的实现了 Runner 和 UI 之间的通信。
- 点击 Start 按钮,通过 FBroadcast 发送起跑消息给 Runner;
- Runner 收到消息后,开始 Run,同时不断通过 FBroadcast 发出 Running info;
- UI 由于注册了接收器,在接收到 Running info 时,通过
FBroadcast.value()获取消息数据,自动更新视图。
整个过程中,Runner 和 UI 之间是完全解耦的,且 UI 只需在 init 中注册接收器(receiver 中调用 setState((){})),就能根据消息数据的变化,自动实时的更新视图,而无需开发者关心整个过程。
场景:点击按钮请求定位,定位成功后接收结果,刷新定位点
class LocationServer {
LocationServer() {
init();
}
init() {
/// register Key_Location receiver
FBroadcast.instance().register(Key_Location, (value, callback) async {
var loc = await location();
/// return message
callback(loc);
});
}
/// Analog positioning
Future<List<double>> location() async {
await Future.delayed(Duration(milliseconds: 2000));
return [Random().nextDouble() * 280, Random().nextDouble() * 150];
}
}
FButton(
...
text: "Location",
onPressed: () {
FLoading.show(context,
color: Colors.black26, loading: buildLoading());
/// request location
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Location,
callback: (location) {
/// The message returned by the receiver
setState(() {
FLoading.hide();
this.location = location;
});
});
},
)
FBroadcast 能够进一步简化需要双向通信的场景。开发者可以看到,在这个例子中,通过 FBroadcast 能够轻松的实现定位请求这种双向通信的场景,而且使得定位服务提供商和UI实现的完全的解耦。
UI交互点只需要发送定位请求的广播,任何注册该广播的定位服务提供商就可以接收该请求进行处理,然后返回结果到UI交互点。也就是说,随着项目的演进,开发者可以随时提供新的定位服务提供商,而无需关心任何的UI变更。
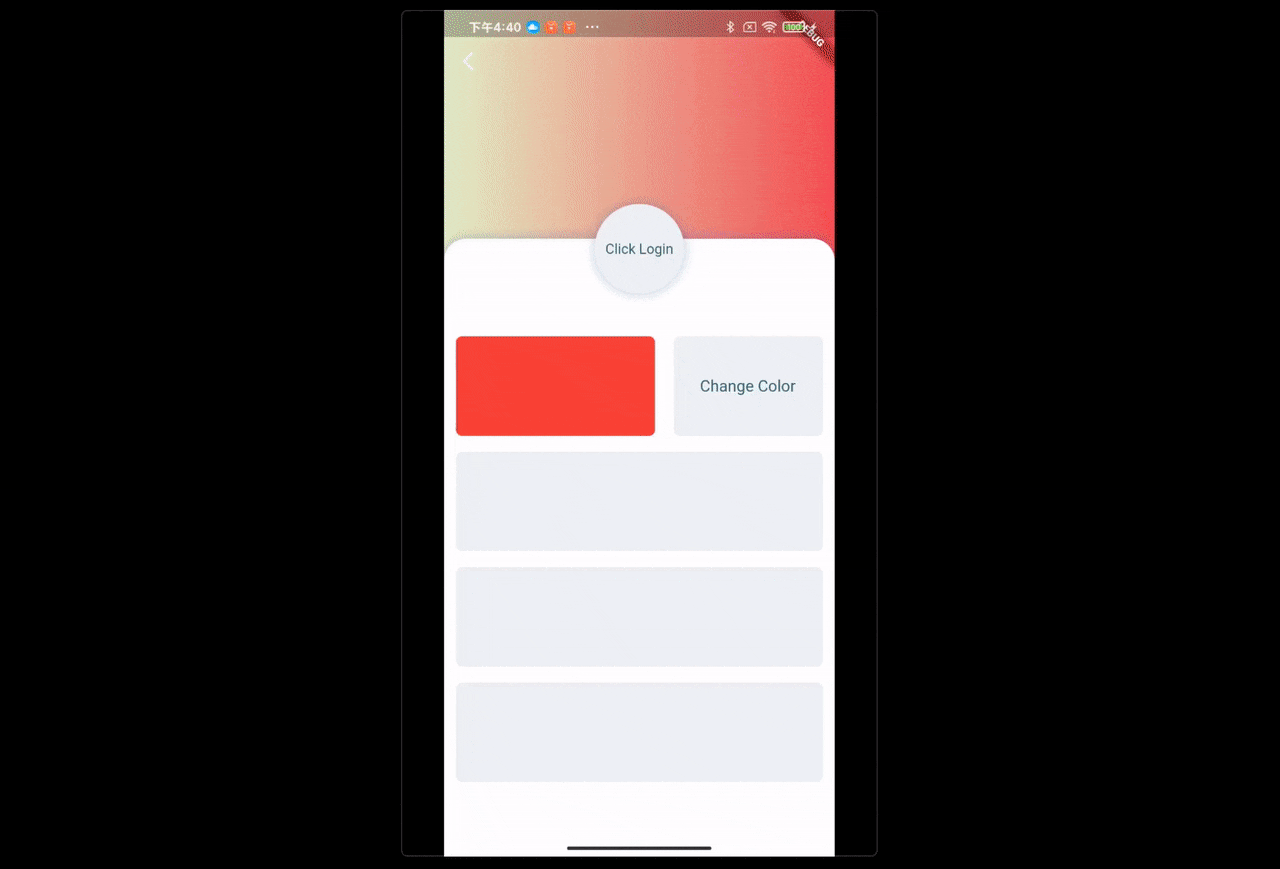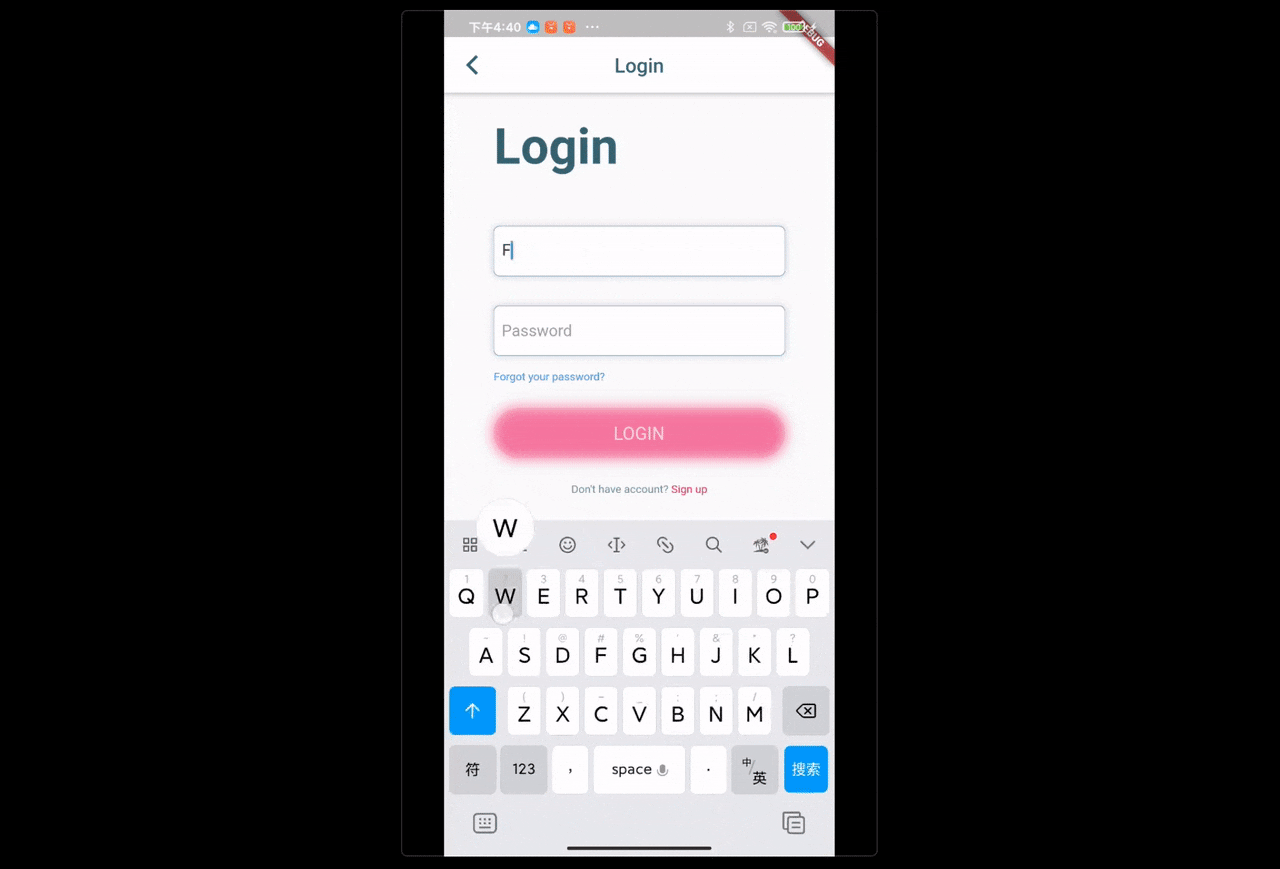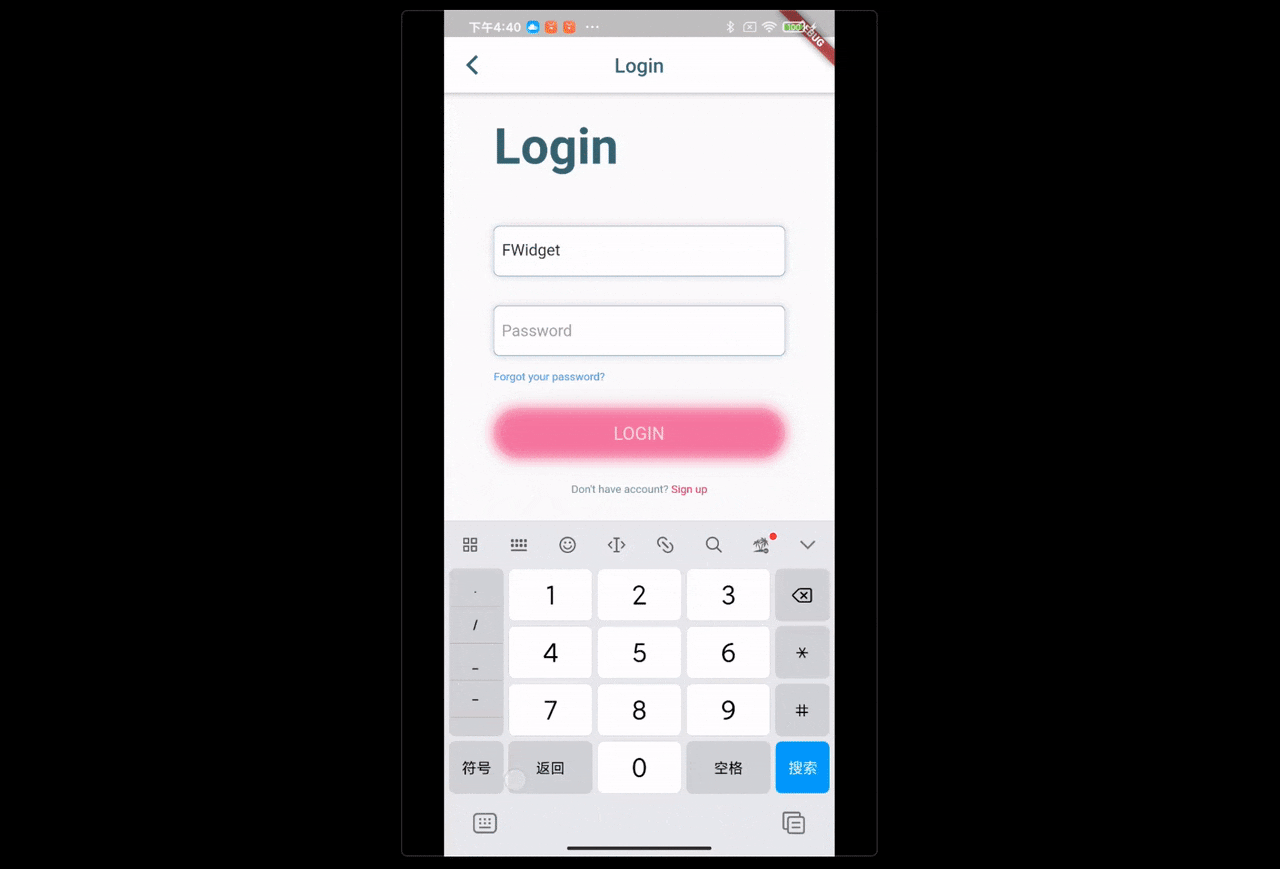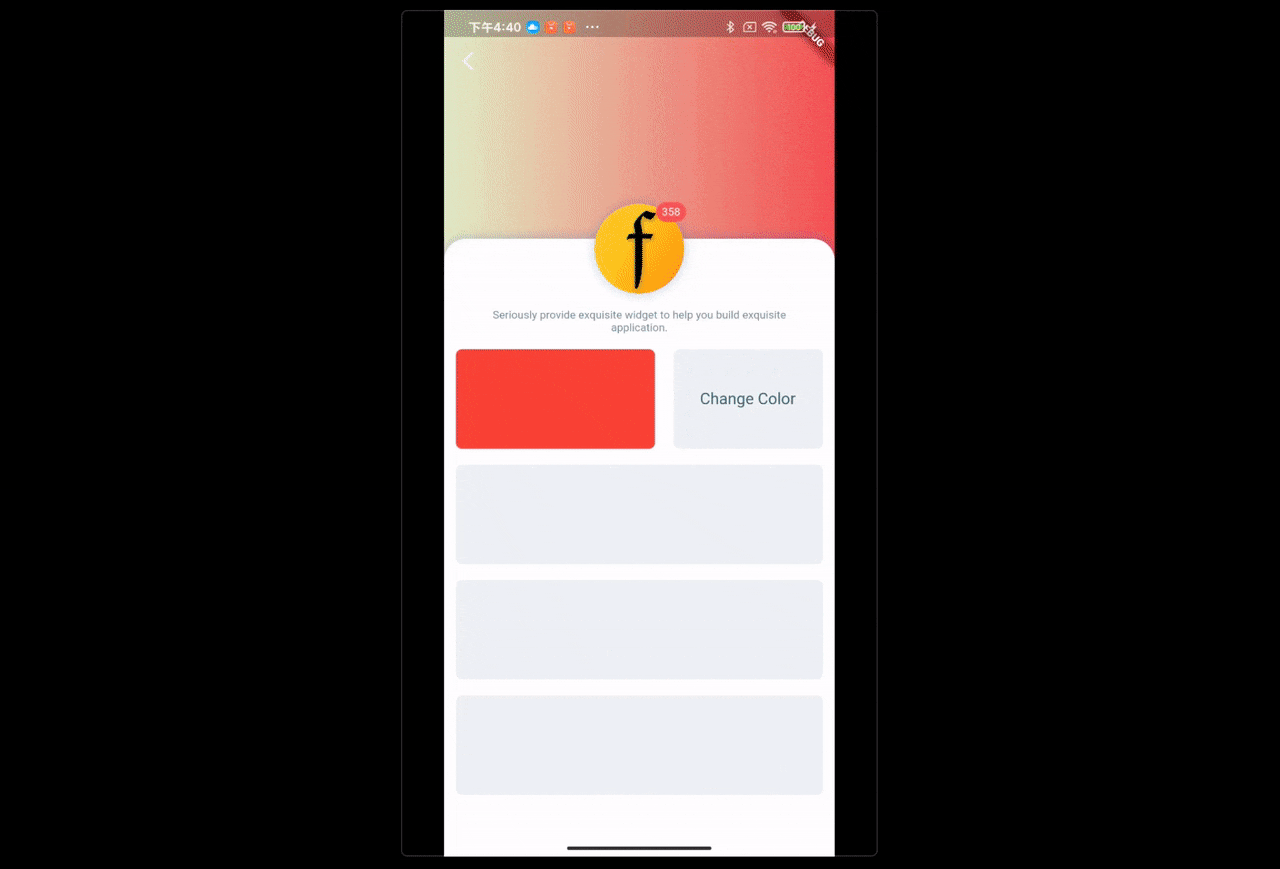
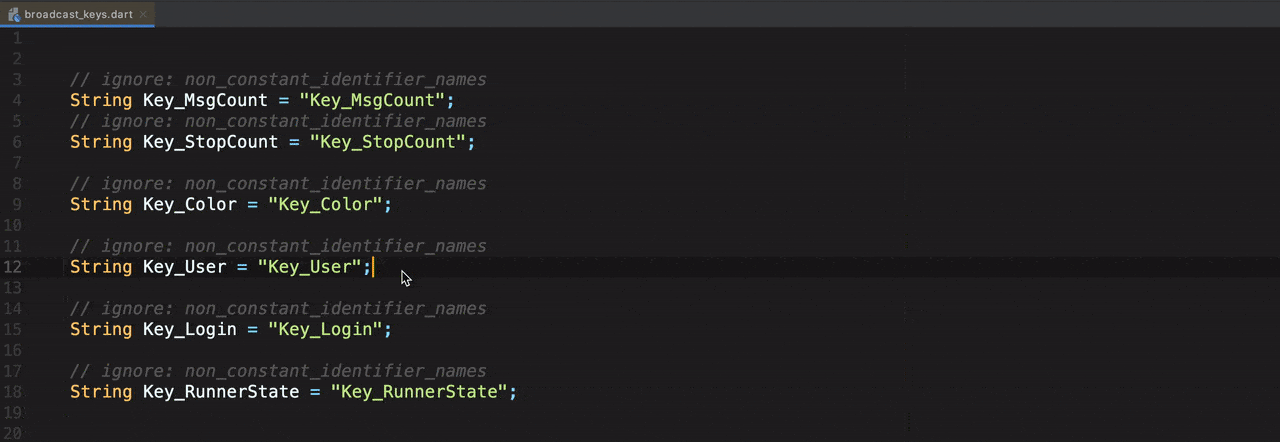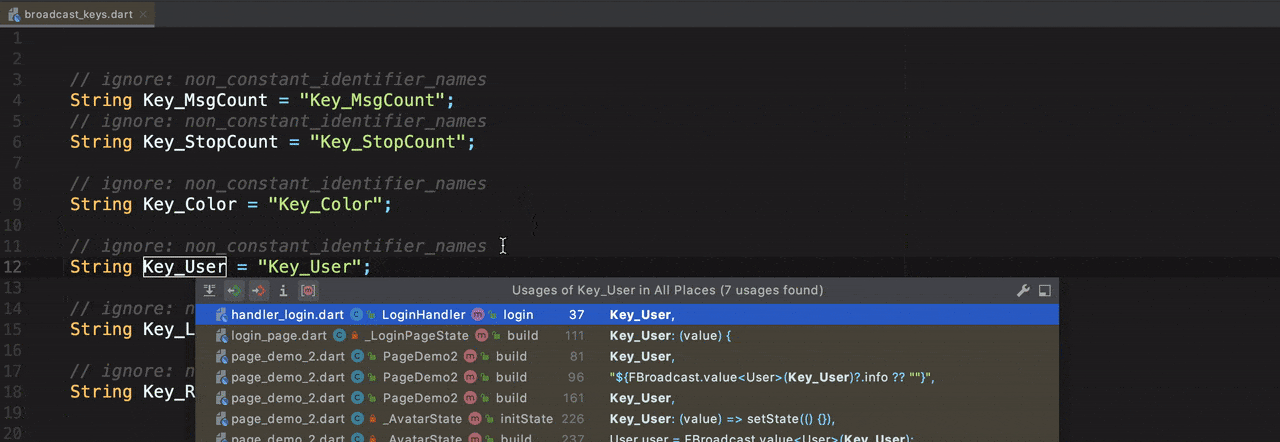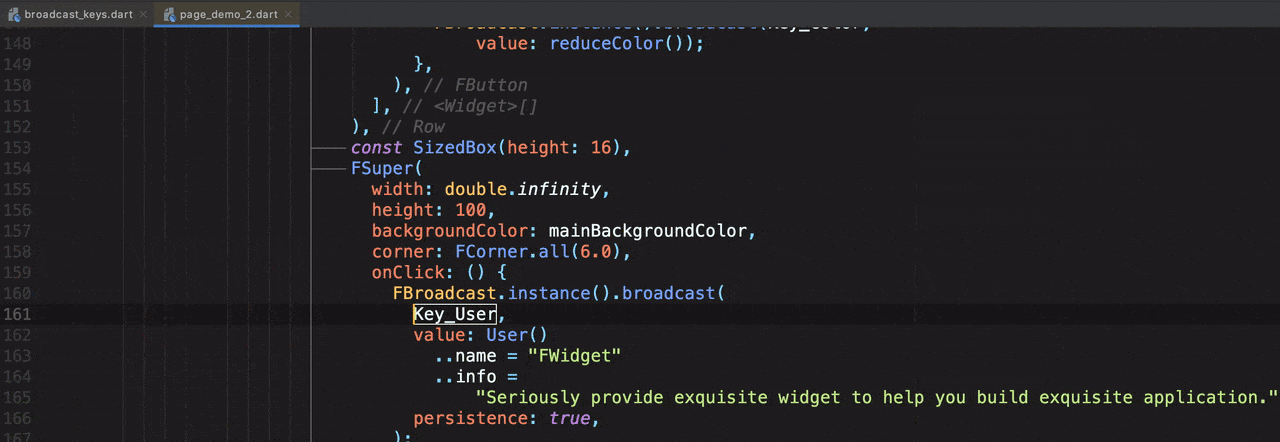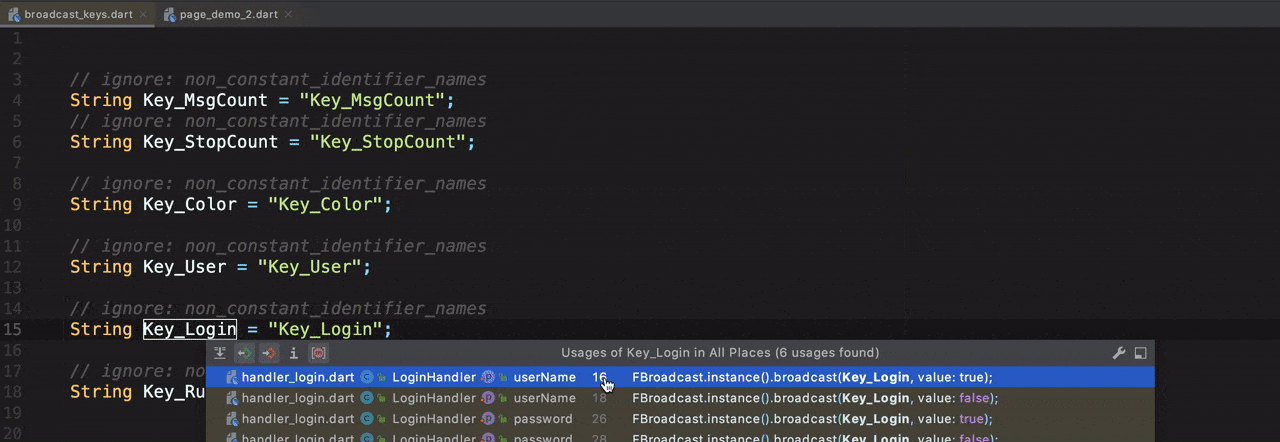
场景:点击改变UI颜色
FButton(
text: "Change Color",
...
onPressed: () {
/// send change color message
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Color, value: reduceColor());
},
)Stateful(
/// init
initState: (setState, data) {
/// register
FBroadcast.instance().register(
Key_Color,
(value, callback) {
/// refresh ui
setState(() {
});
},
/// bind context
context: data,
);
},
builder: (context, setState, data) {
return FSuper(
...
/// get color value
backgroundColor: FBroadcast.value<Color>(Key_Color) ?? mainBackgroundColor,
);
},
)通过 FBroadcast 可以很轻易的完成 UI 交互之间的局部状态更新。上面的示例展示了颜色的变更,数据对象只有一个参数,实际开发过程中,开发者可以根据需要将通信的数据对象进行丰富扩展。
开发者只需要在需要更新 UI 的 Widget 中注册接收器,调用一次 setState((){}),在交互点发出消息。而不用去主动的将触发逻辑和 setState((){}) 在所有的交互点都写一次。
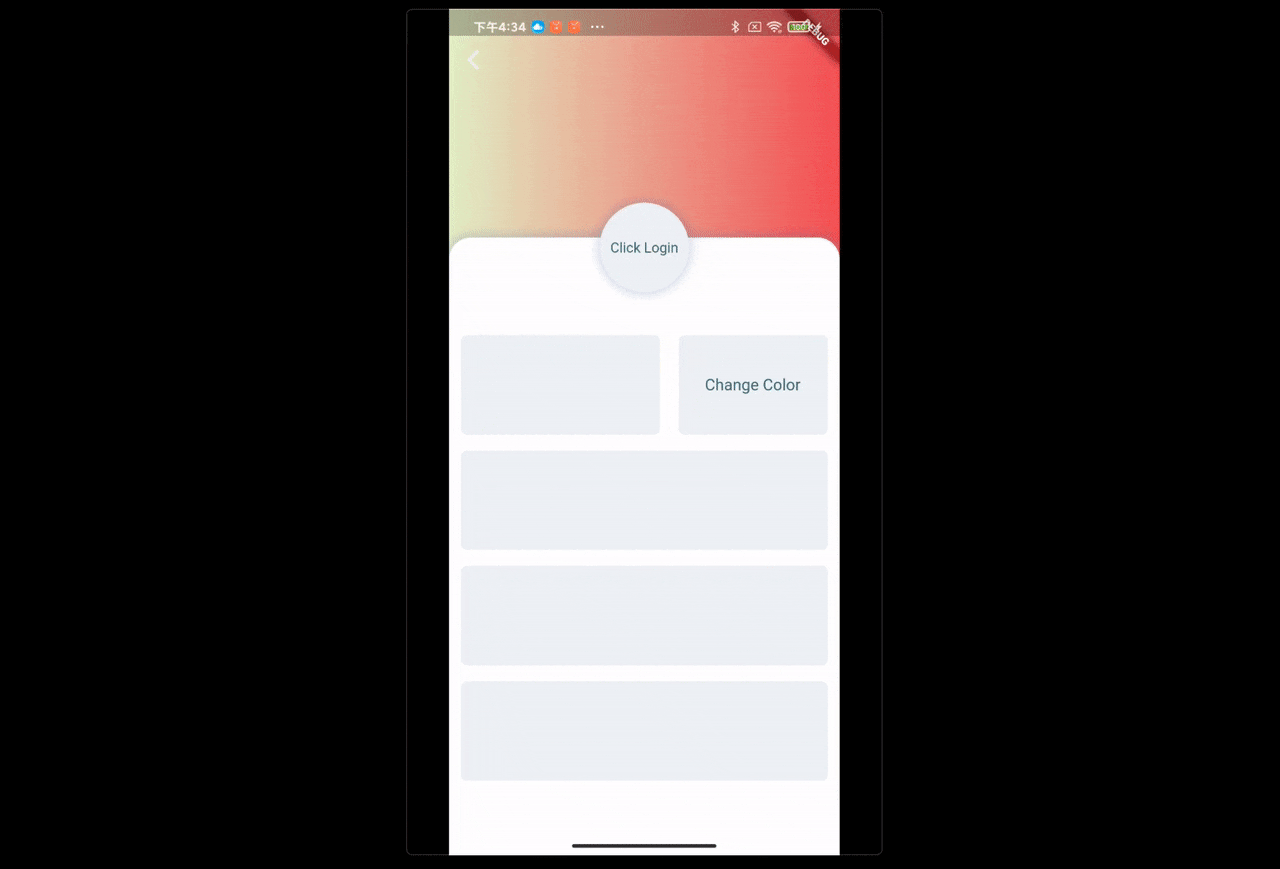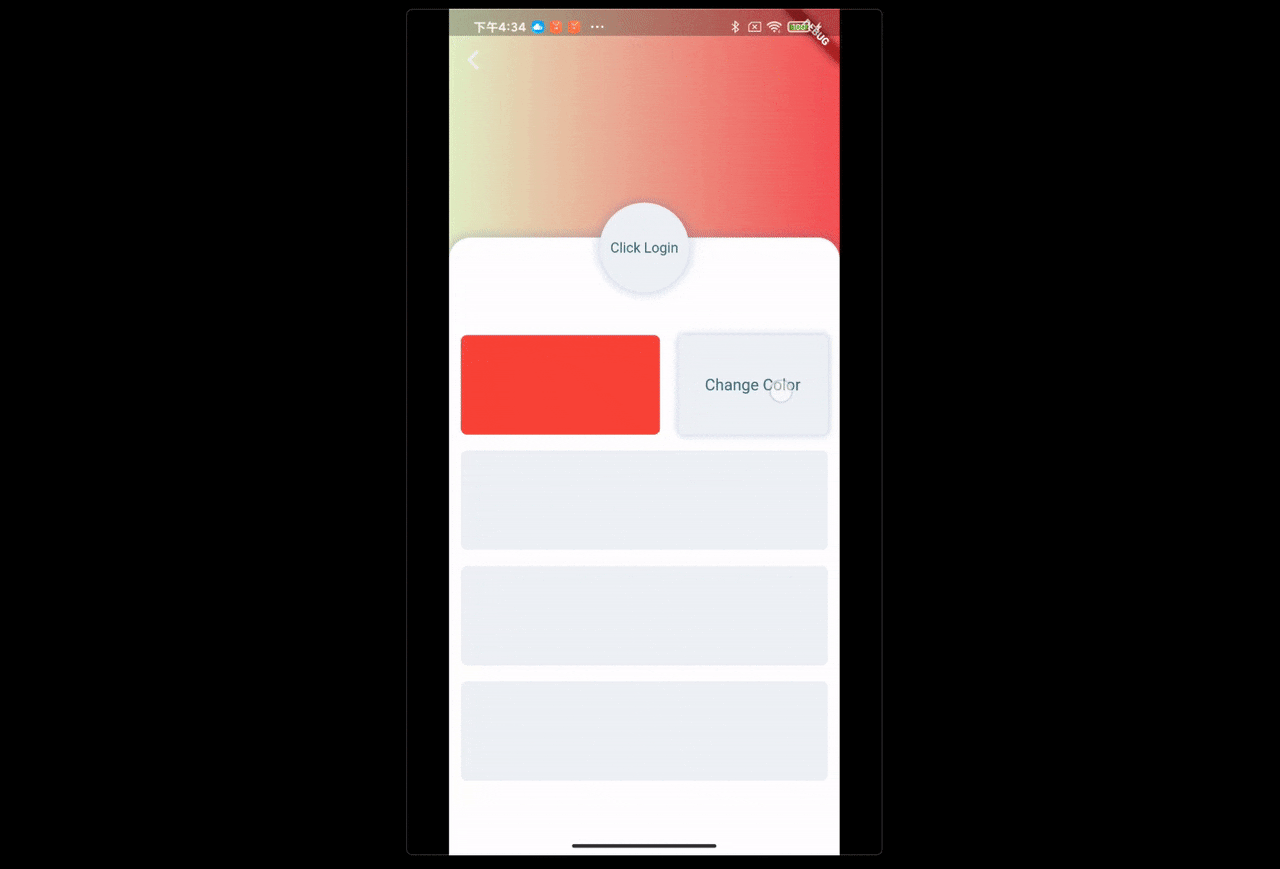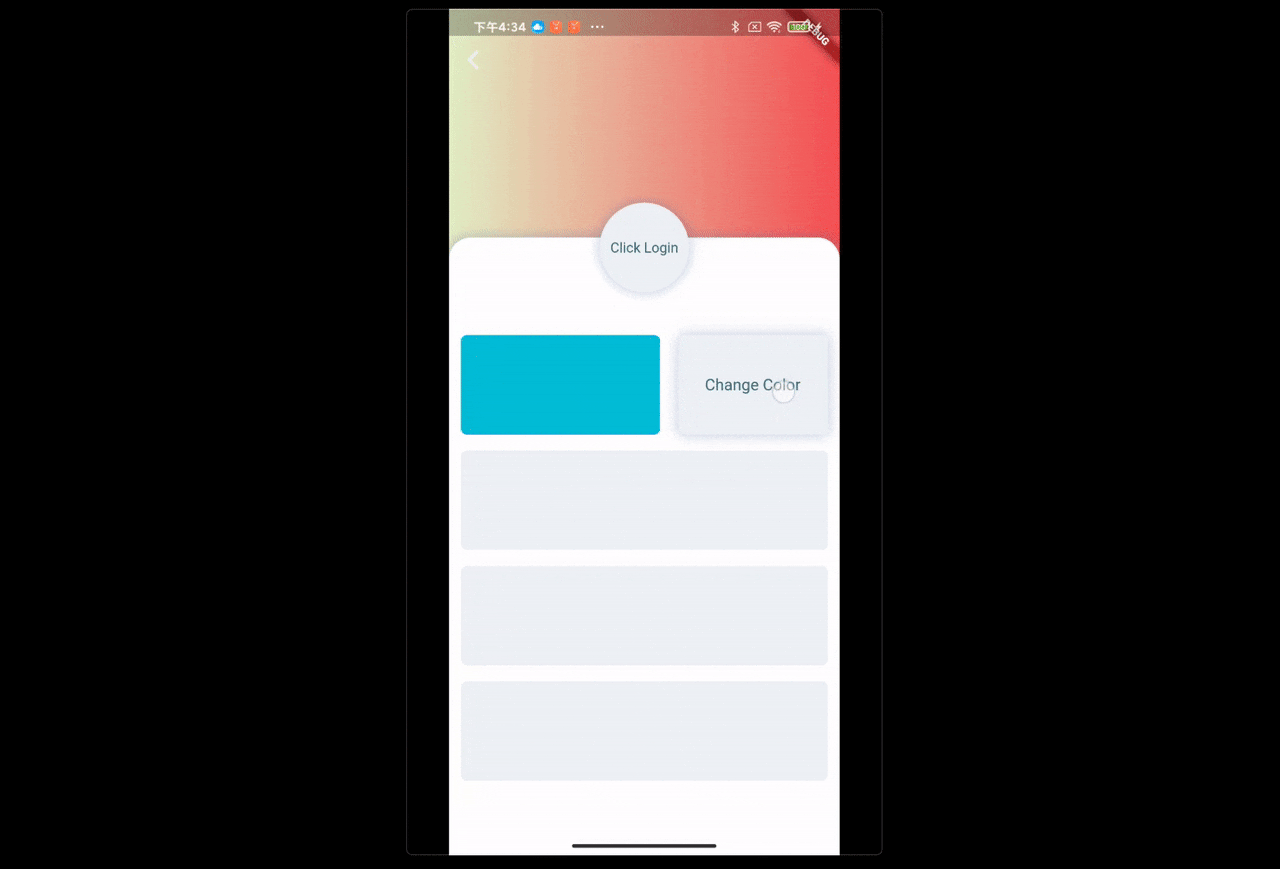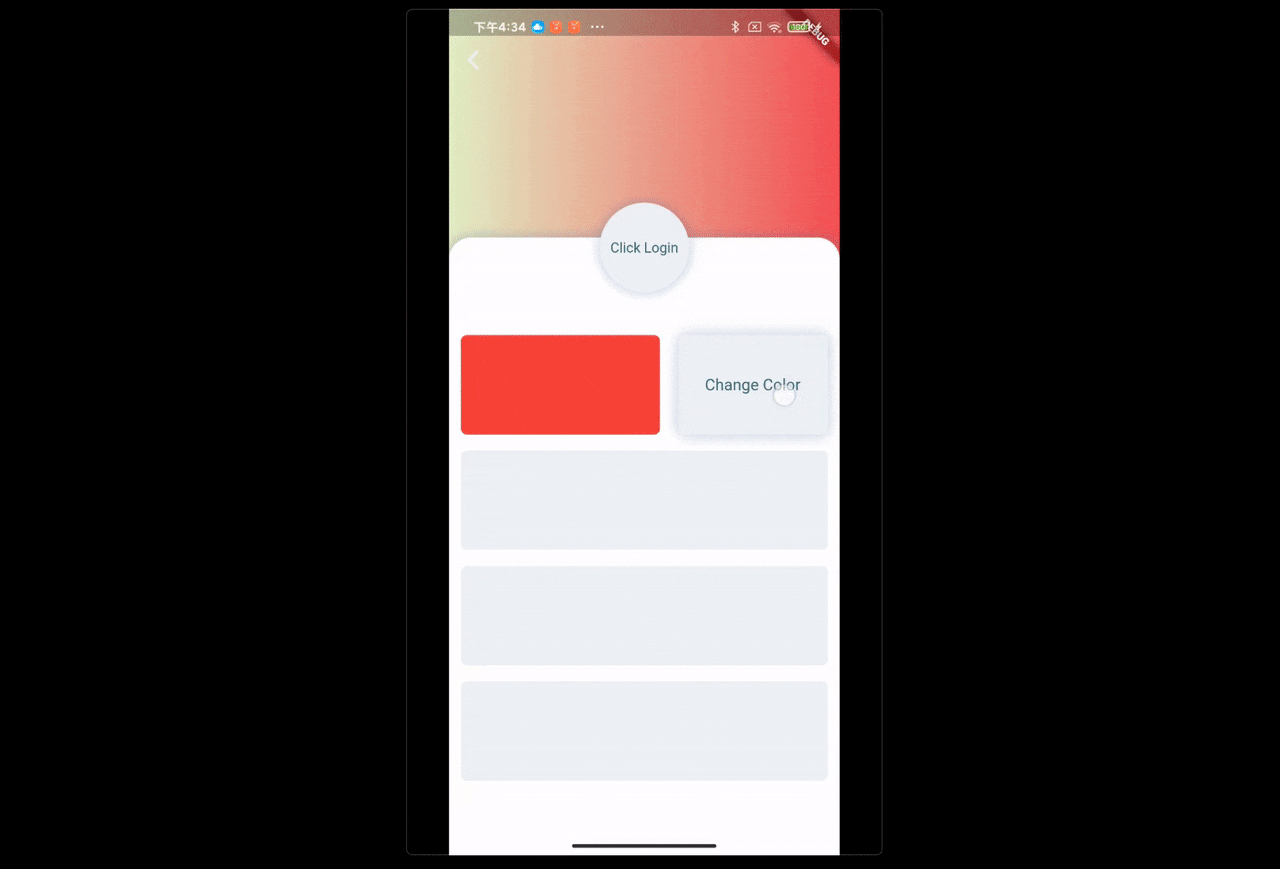
场景:点击头像跳转登陆页,当账号密码不为 null 时,登陆按钮才可以点击。点击登陆按钮发送登陆请求,登陆成功后,返回上一页,刷新用户信息。
class Avatar extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_AvatarState createState() => _AvatarState();
}
class _AvatarState extends State<Avatar> {
User user;
int msgCount = 0;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
FBroadcast.instance().register(
Key_MsgCount,
/// register Key_MsgCount reviver
(value, callback) => setState(() {
msgCount = value;
}),
more: {
/// register Key_User reviver
Key_User: (value, callback) => setState(() {
/// get value
user = value;
}),
},
/// bind context
context: this,
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return FSuper(
...
backgroundImage: (user == null || _textIsEmpty(user.avatar)) ? null : AssetImage(user.avatar),
redPoint: user != null && msgCount > 0,
redPointText: msgCount.toString(),
text: user != null ? null : "Click Login",
onClick: user != null
? null
: () => Navigator.push(context, MaterialPageRoute( builder: (context) => LoginPage())),
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
super.dispose();
/// remove all receivers from the environment
FBroadcast.instance().unregister(this);
}
}登陆页中注册 Key_User 接收器,当接收到登陆消息时,取出其中的数据,刷新UI。
class User{
String name;
String avatar;
int messageCount = 0;
String info;
}class LoginHandler {
String _userName;
String _password;
/// set user name, check to see if login is allowed
set userName(String v) {
_userName = v;
if (_textNoEmpty(_userName) && _textNoEmpty(_password)) {
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Login, value: true);
} else {
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Login, value: false);
}
}
/// set user password, check to see if login is allowed
set password(String v) {
_password = v;
if (_textNoEmpty(_userName) && _textNoEmpty(_password)) {
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Login, value: true);
} else {
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(Key_Login, value: false);
}
}
/// login
void login() {
Timer(Duration(milliseconds: 1500), () {
/// login success,send login success message —— Key_User
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(
Key_User,
value: User()
..avatar = "assets/logo.png"
..name = _userName
..info =
"Seriously provide exquisite widget to help you build exquisite application.",
/// Persistence Key_User
persistence: true,
);
});
}
}将逻辑处理转移到 LoginHandler 中进行隔离,所有的处理结果都通过 FBroadcast 广播出去,使注册到广播系统中的对应接收器能够响应。
class LoginPage extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_LoginPageState createState() => _LoginPageState();
}
class _LoginPageState extends State<LoginPage> {
/// Logic handler
LoginHandler handler = LoginHandler();
/// input controller
FSearchController _controller1 = FSearchController();
FSearchController _controller2 = FSearchController();
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
_controller1.setListener(() {
/// update userName
handler.userName = _controller1.text;
});
_controller2.setListener(() {
/// update password
handler.password = _controller2.text;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return {
...
/// userName input
FSearch(
controller: _controller1,
...
),
...
/// userName input
FSearch(
controller: _controller2,
...
),
...
Stateful(
initState: (setState, data) {
/// register login receiver
FBroadcast.instance().register(
Key_Login,
/// refresh ui
(value, callback) => setState(() {}),
more: {
/// register user receiver
Key_User: (value, callback) {
FLoading.hide();
Navigator.pop(context);
},
},
/// bind context
context: data,
);
},
builder: (context, setState, data) {
return FButton(
...
text: "LOGIN",
/// Key_Login value=true is allowed to click login
onPressed: !(FBroadcast.value(Key_Login) ?? false)
? null
: () {
_controller1.clearFocus();
_controller2.clearFocus();
FLoading.show(context);
/// Execute login logic
handler.login();
},
);
},),
...
};
}
}注册接收器时,只需在接收回调中调用 setState((){}),后续所有的数据变化刷新,开发者就可以不用关注了。而给 UI 赋值可以方便的通过 FBroadcast.value() 获取对应数据来进行。
⚠️ 注意,对于需要全局使用的状态/数据模型,它们对应的广播类型,在发送时,需要至少有一次将 persistence 设置为 true。上面示例中,就在登陆成功后,对Key_User类型的广播进行了持久化。
/// login success,send login success message —— Key_User
FBroadcast.instance().broadcast(
Key_User,
value: User()
..avatar = "assets/logo.png"
..name = _userName
..info =
"Seriously provide exquisite widget to help you build exquisite application.",
/// Persistence Key_User
persistence: true,
);上面的示例中展示了通过 FBroadcast 可以轻松快速的实现消息传递,进行 局部、全局状态管理和刷新,很好的将各个模块,逻辑以及UI 进行解耦。FBroadcast 提供了简洁易懂,而且十分灵活的广播系统,极少的束缚让开发者可以快速上手,轻松实现复杂逻辑的简化,帮助开发者构建出易于维护的、复杂的、精美的应用。
FBroadcast 在使用过程中,配合统一的广播类型注册表(也可以按模块分多张),开发者可以很轻易的借助 IDEA 的引用检索能力,随时查看所有广播的情况,对于不断迭代过程中的维护十分有益。
/// 注册指定类型的接收者。
/// 如果传入了 [context] 环境,该接收者将会被注册到环境中。环境可以是任意类型的对象,例如:页面、类..
/// 接收者通过 [value] 可以获取到本条消息携带的数据。
/// 当调用 [unregister] 时,该接收者即会被清除。
/// [key] - 消息类型
/// [receiver] - 接收者
/// [context] - 环境。不为null,[receiver] 将会被注册到环境中。
/// [more] - 方便一次注册多个接收者
///
/// Register recipients of the specified type.
/// If the [context] environment is passed in, the recipient will be registered in the environment. The environment can be any type of object, for example: page, class...
/// The receiver can get the data carried in this message through [value].
/// When [unregister] is called, the receiver will be cleared.
/// [key]-message type
/// [receiver] - receiver
/// [context] - context. Not null, [receiver] will be registered in the environment.
/// [more] - Make it easy to register multiple recipients at once
FBroadcast register(String key, ResultCallback receiver, {Object context, Map<String, ResultCallback> more})/// 广播一条 [key] 类型的消息。
/// 已经注册在系统中的接收者将会接收到本条消息。
/// 接收者通过 [value] 可以获取到本条消息携带的数据。
/// [key] - 消息类型
/// [value] - 消息携带的数据。可以是任意类型或是null。
/// [callback] - 能够收到接收器返回的消息
/// [persistence] - 是否持久化消息类型。持久化的消息可以在任意时刻通过 [FBroadcast.value] 获取当前消息的数据包。默认情况下,未持久化的消息类型在没有接收者的时候会被移除,而持久化的消息类型则不会。开发者可以通过 [clear] 函数来移除持久化的消息类型。
///
/// Broadcast a message of type [key].
/// Recipients already registered in the system will receive this message.
/// The receiver can get the data carried in this message through [value].
/// [key] - Message type
/// [value] - The data carried in the message. Can be any type or null.
/// [callback] - Able to receive the message returned by the receiver
/// [persistence] - Whether or not to persist message types. Persistent messages can be retrieved at any time by [FBroadcast. Value] for the current message packet. By default, unpersisted message types are removed without a receiver, while persisted message types are not. Developers can use the [clear] function to remove persistent message types.
void broadcast(String key, {dynamic value, ValueCallback callback, bool persistence = false})/// 广播一条 [key] 类型的粘性消息。
/// 如果广播系统中还有没注册该类型的接收者,本条消息将被滞留在系统中。一旦有该类型接收者被注册,本条消息将会被立即发送给接收者。
/// 如果系统中已经注册有该类型的接收者,本条消息将会被立即发送给接收者。
/// 接收者通过 [value] 可以获取到本条消息携带的数据。
/// [key] - 消息类型
/// [value] - 消息携带的数据。可以是任意类型或是null。
/// [callback] - 能够收到接收器返回的消息
/// [persistence] - 是否持久化消息类型。持久化的消息可以在任意时刻通过 [FBroadcast.value] 获取当前消息的数据包。默认情况下,未持久化的消息类型在没有接收者的时候会被移除,而持久化的消息类型则不会。开发者可以通过 [clear] 函数来移除持久化的消息类型。
///
/// Broadcast a sticky message of type [key].
/// If there are unregistered receivers of this type in the broadcast system, this message will be stuck in the system. Once a recipient of this type is registered, this message will be sent to the recipient immediately.
/// If this type of receiver is already registered in the system, this message will be sent to the receiver immediately.
/// The receiver can get the data carried in this message through [value].
///
/// [key] - Message type
/// [value] - The data carried in the message. Can be any type or null.
/// [callback] - Able to receive the message returned by the receiver
/// [persistence] - Whether or not to persist message types. Persistent messages can be retrieved at any time by [FBroadcast. Value] for the current message packet. By default, unpersisted message types are removed without a receiver, while persisted message types are not. Developers can use the [clear] function to remove persistent message types.
void stickyBroadcast(String key, {dynamic value, ValueCallback callback, bool persistence = false})/// 接收者可以通过该函数获取消息中的数据
///
/// This function allows the receiver to get the data in the message
static T value<T>(String key)/// 移除指定的接收者 [receiver]。
/// 如果指定了 [key]、[context] 将有助于更快的移除指定接收者。
/// [receiver] - 接收者
/// [key] - 消息类型
/// [context] - 环境。
///
/// Remove the specified receiver [receiver].
/// If [key] and [context] are specified, it will help to remove the specified recipient faster.
/// [receiver] - receiver
/// [key]-message type
/// [context] - context.
FBroadcast remove(ResultCallback receiver, {String key, Object context})/// 移除广播系统中的指定 [key] 类型的所有接收者,以及该类型的粘性广播。
/// [key] - 类型
///
/// Remove all receivers of the specified [key] type in the broadcast system and sticky broadcasts of that type.
/// [key] - type
void clear(String key)/// 移除广播系统中,注册到 [context] 环境内的所有接收者。
/// 例如,在页面关闭时,开发者可以通过 [unregister] 一次性移除注册到该环境内的所有接收者。
/// 当然,前提时在接收者通过 [register] 注册的时候,传入 [context],将接收者注册到该环境中。
/// [context] - 环境。
///
/// Remove all receivers registered in the [context] environment from the broadcast system.
/// For example, when the page is closed, the developer can use [unregister] to remove all recipients registered in the environment at once.
/// Of course, the prerequisite is that when the receiver registers through [register], pass in [context] to register the receiver to the environment.
/// [context] - context.
void unregister(Object context)/// 会移除广播系统中的所有的接收者,以及粘性广播。
///
/// Remove all receivers in the broadcasting system, and sticky broadcasting.
void dispose()在项目 pubspec.yaml 文件中添加依赖:
dependencies:
fbroadcast: ^<版本号>
⚠️ 注意,请到 pub 获取 FBroadcast 最新版本号
dependencies:
fbroadcast:
git:
url: '[email protected]:Fliggy-Mobile/fbroadcast.git'
ref: '<分支号 或 tag>'
⚠️ 注意,分支号 或 tag 请以 FBroadcast 官方项目为准。
Copyright 2020-present Fliggy Android Team <[email protected]>.
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at following link.
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License.
感觉还不错?请投出您的 Star 吧 🥰 !
1.clone 工程到本地
2.进入工程 example 目录,运行以下命令
flutter create .
3.运行 example 中的 Demo