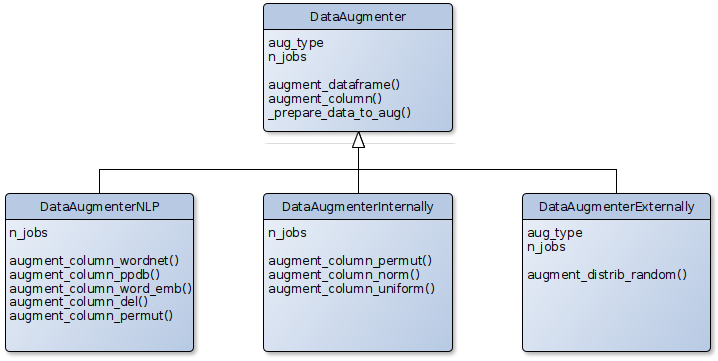
Zarnitsa package with data augmentation tools.
- Internal data augmentation using existed data
- External data augmentation setting known statistical distributions by yourself
- NLP augmentation
- Python3
- numpy
- pandas
- nlpaug
- wget
- scikt-learn
Install package using PyPI:
pip install zarnitsa
Or using actual github repo:
pip install git+https://github.com/AlexKay28/zarnitsa
Simple usage examples:
This is type of augmentation which you may use in case of working with numerical features.
>>> from zarnitsa.DataAugmenterInternally import DataAugmenterInternally
>>> daug_comb = DataAugmenterInternally()
>>> aug_types = [
>>> "normal",
>>> "uniform",
>>> "permutations",
>>> ]
>>> # pd Series object example
>>> s = pd.Series([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
>>> for aug_type in aug_types:
>>> print(aug_type)
>>> print(daug_comb.augment_column(s, freq=0.5, return_only_aug=True, aug_type=aug_type))
normal
7 9.958794
3 0.057796
0 -3.135995
6 7.197400
8 13.258087
dtype: float64
uniform
2 10.972232
8 5.335357
9 9.111281
5 5.964971
4 -0.210732
dtype: float64
permutations
4 6
5 4
9 10
3 3
2 5
dtype: int64
This is type of augmentation which you may use in case of working with textual information.
>>> from zarnitsa.DataAugmenterNLP import DataAugmenterNLP
>>> daug = DataAugmenterNLP()
>>> text = "This is sentence example to augment. Thank you for interesting"
>>> daug.augment_column_wordnet(text)
'This be sentence example to augment. Thank you for concern'
>>> daug.augment_column_del(text, reps=1)
'This is sentence example to augment. you for interesting'
>>> daug.augment_column_permut(text, reps=1)
'This sentence is example to augment. Thank you for interesting'
This is type of augmentation which you may use in case of working with distribution modeling having prior knowlege about it
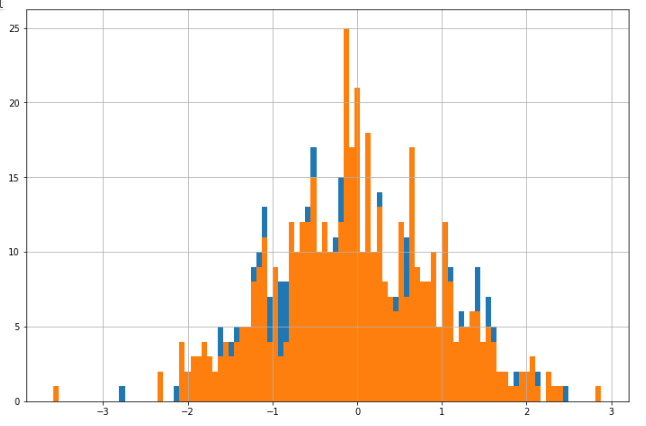
Doing df[...] = np.nan we imitate data sparsness or misses which we try to fill up using augmentations
>>> size = 500
>>> serial_was = pd.Series(daug.augment_distrib_random(aug_type='normal', loc=0, scale=1, size=size))
>>> serial_new = copy(serial_was)
>>> serial_new.loc[serial_new.sample(100).index] = None
>>> serial_new = daug.augment_column(serial_new, aug_type='normal', loc=0, scale=1)
>>> plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
>>> serial_was.hist(bins=100)
>>> serial_new.hist(bins=100)
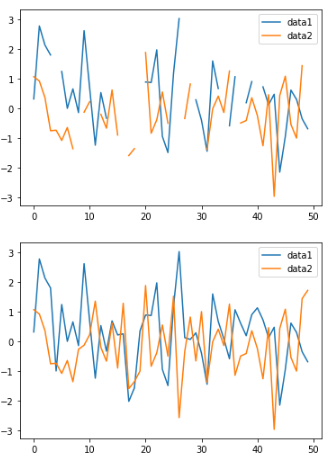
>>> size=50
>>> df = pd.DataFrame({
>>> 'data1': daug.augment_distrib_random(aug_type='normal', loc=0, scale=1, size=size),
>>> 'data2': daug.augment_distrib_random(aug_type='normal', loc=0, scale=1, size=size),
>>> })
>>> for col in df.columns:
>>> df[col].loc[df[col].sample(10).index] = None
>>> plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
>>> df.plot()
>>> daug.augment_dataframe(df, aug_type='normal', loc=0, scale=1).plot()