Cardiothoracic Disease Diagnosis: Using Machine Learning for Accurate Disease Detection from Chest Scans
Cardiovascular diseases were rare before the 20th century, but have become the leading cause of death worldwide since the 1960s. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment, but interpreting chest scans can be challenging, leading to misdiagnoses. Additionally, in underprivileged communities, chest x-rays serve as a bottleneck in diagnoses. To address this challenge, we applied a 2D convolutional neural network to diagnose cardiothoracic diseases. Furthermore, we employed inductive transfer learning of YOLOv7 and EfficientDet and designed a customized DETR transformer model for detection of health issues that lie within the patient's scan. During this, we focused on treating three conditions: Cardiomegaly, Pneumonia, and Covid-19. Cardiomegaly is a key indicator of potential heart disease which can be difficult to detect in chest radiographs due to its subtle presentation. We also decided to look into Covid-19 and Pneumonia, given their prevalence in today's population and the significant impact they have on mortality rates.
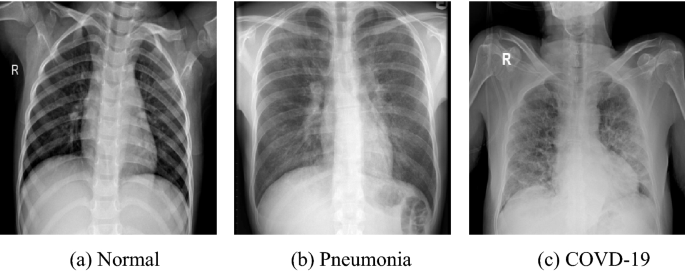
This is an example of our training data
To create our main dataset for training, we gathered data from various sources, including the NCBI and National Institute of Health. Each image was preprocessed with a bounding box to indicate the disease location. With this data, we trained our models to accurately detect COVID-19, Pneumonia, and Cardiomegaly in chest scans. We used industry-standard data augmentation techniques, such as random cropping, rotation, and horizontal flips, to diversify our data and generate a larger pool of accurate data as well as account for the fewer data available for Cardiomegaly. These augmentation methods enabled us to signficiantly increase our data pool with data that accurately reflects the common complexities and impurities in diagnostic imaging.
This is an example of our augmented/synthetic data
Our Choices of Models:
- DETR (Detection Transformer): DETR, or Detection Transformer, is a cutting-edge object detection framework that utilizes a transformer-based architecture to reason about the relationship of objects and the global context of the image. Unlike traditional object detection algorithms that rely on region proposal networks and post-processing steps, DETR directly predicts the set of objects present in an image as well as their corresponding bounding boxes in a single forward pass. This approach eliminates the need for heuristic post-processing steps and enables end-to-end training of the model. The backbone of DETR consists of a ResNet-50, which is a popular convolutional neural network architecture for image classification tasks. However, to combine the strengths of global and local feature extraction, we have developed a ResNet-50/EfficientNet hybrid backbone. This allows the model to extract both low-level and high-level features from the input image, which improves the overall performance of the detector. The DETR framework has shown remarkable results on the COCO benchmark and has demonstrated its potential for real-world applications such as robotics, autonomous driving, and surveillance.
Original Model: https://github.com/facebookresearch/detr - YOLOv7: YOLOv7 is a state-of-the-art object detection algorithm that has gained significant attention in recent years due to its high efficiency and accuracy. This model serves as an industry-standard detection model, and its comparison with the customized DETR transformer provides us with valuable insights into the performance of different object detection approaches. The YOLOv7 model achieves high efficiency by using a single neural network to predict the bounding boxes and class probabilities of all objects in an image simultaneously. This approach reduces the computational complexity of the algorithm and enables real-time object detection in video streams. By comparing the performance of YOLOv7 with our customized DETR transformer, we can evaluate the effectiveness of each method in various scenarios and determine the optimal approach for specific applications. This enables us to develop customized object detection models that can cater to the unique needs of different industries and use cases
Original Model: https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7 - EfficientDET: EfficientDet is a state-of-the-art object detection algorithm that achieves high accuracy while being computationally efficient. It is designed to address the trade-off between accuracy and efficiency in object detection tasks, which are crucial for a variety of applications such as autonomous driving, robotics, and surveillance. EfficientDet uses a novel compound scaling method that optimizes the network architecture, input image resolution, and model depth to achieve better accuracy and efficiency simultaneously. It also uses efficient building blocks such as mobile inverted bottleneck convolution (MBConv) and squeeze-and-excitation (SE) modules to reduce the computational cost while maintaining high performance. The EfficientDet models have achieved top performance on the COCO benchmark, which evaluates object detection accuracy and efficiency, and have been widely adopted in real-world applications due to their high efficiency and accuracy.
Our Custom DETR Backbone
- Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve (ROC)
- Confusion Matrix
DETR Loss Analysis
The DETR model has two loss components:
- Classification loss penalizes incorrect object predictions, and is calculated using cross‐entropy between predicted class probabilities and true labels.
- Bounding box regression loss minimizes the difference between predicted and ground‐truth boxes, and is calculated using a distance measure like L1 or L2 distance.
The overall DETR loss function balances classification and regression losses to optimize object detection and localization in images. At a 98.1% accuracy, the custom DETR model outperformed the base DETR model’s accuracy of 92.3%, YOLOv7’s accuracy of 96.2%, and Efficient‐Det’s 95.6% accuracy.
As we continue to refine our machine learning model for cardiothoracic diagno‐ sis, there are several potential future endeavors that we can pursue. One such area of exploration is the use of more detailed data sources representative of other chest‐related diseases along with more patient information. Additionally, we plan to implement EfficientDET, an object detection model that is optimized for lightweight devices for the development of a mobile application that utilizes our model for real‐time diagnosis of cardiothoracic diseases. This could greatly improve access to healthcare in underprivileged communities. Overall, there is much room for growth and innovation in the field of cardiothoracic diagnosis, and we look forward to continuing our efforts in this exciting area of research
-
Carion, N., Massa, F., Synnaeve, G., Usunier, N., Kirillov, A., & Zagoruyko, S. (2020). End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2005.12872.pdf
-
DE⫶TR: End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers. (2022, October 27). GitHub. https://github.com/facebookresearch/detr
-
He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2015). Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385v1.pdf
-
Moses, D. A. (2021). Deep learning applied to automatic disease detection using chest X‐rays. Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology, 65(5), 498–517. https://doi.org/10.1111/1754-9485.13273
-
Santosh, K. C., Dhar, M. K., Rajbhandari, R., & Neupane, A. (2020, July 1). Deep Neural Network for Foreign Object Detection in Chest X-Rays. IEEE Xplore. https://doi.org/10.1109/CBMS49503.2020.00107
-
Tan, M., Pang, R., & Le, Q. (2020). EfficientDet: Scalable and Efficient Object Detection. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.09070.pdf
-
Wang, C.-Y., Bochkovskiy, A., & Liao, H.-Y. (2022). YOLOv7: Trainable bag-of-freebies sets new state-of-the-art for real-time object detectors. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2207.02696.pdf